Expression of TRF2 and its prognostic relevance in advanced stage cervical cancer patients
- PMID: 25654471
- PMCID: PMC4335779
- DOI: 10.1186/0717-6287-47-61
Expression of TRF2 and its prognostic relevance in advanced stage cervical cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Telomeres are protective caps consisted of specific tandem repeats (5'-TTAGGG-3'). Shortening of telomeres at each cell division is known as "mitotic clock" of the cells, which renders telomeres as important regulators of lifespan. TRF2 is one of the critical members of shelterin complex, which is a protein complex responsible from the preservation of cap structure, and loss or mutation of TRF2 results in DNA damage, senescence or apoptosis. Since cancer is frequently associated with aberrant cell cycle progression, defective DNA repair or apoptosis pathways, TRF2 could be one likely candidate for cancer therapy. Here we investigated the prognostic role of TRF2 levels in cervical cancer patients. Fold-induction rates were evaluated with respect to median values after real-time PCR analysis. Overall survival, distant disease-free and local recurrence-free survival rates were calculated using Kaplan-Meier long rank test.
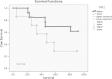
Results: Both five year overall- and disease-free survival rates were longer in patients with higher TRF2 expression compared to lower expression, but results were not statistically significant (69.2% vs 28.9%, respectively). Mean local recurrence-free survivals (LRF) were very close ( 58.6, CI: 44.3-72.9 vs 54.5, CI: 32.1-76.9 months) for high and low expressions, respectively. Cumulative proportion of LRF at the end of five year period was 76.9% for high and 57.1% for low TRF2 expression (P = 0.75). Statistically significant difference was found between survival ratios and Bcl-xL and p53 gene expressions, but not with TRF2. A respectable correlation between TRF2 expression and apoptosis along with distant metastasis was noted (P = 0.045 and 0.036, respectively). Additionally, high TRF2 expression levels had a positive impact in five year survival rate of stage IIIB-IVA patients (P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Our results support the role of TRF2 in apoptosis and imply a positive relation with distant metastases and survival in advanced stage patients. The remarkable difference in survival periods of patients with different TRF2 expressions suggest that TRF2 may be a candidate factor to estimate survival for cervical cancer, a preliminary observation which should further be verified with a larger cohort.
Figures
References
-
- Hougardy BM, Maduro JH, van der Zee AG, Willemse PH, De Jong S, De Vries EG. Clinical potential of inhibitors of survival pathways and activators of apoptotic pathways in treatment of cervical cancer: changing the apoptotic balance. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:589–598. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70281-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous