Characterizing sialic acid variants at the glycopeptide level
- PMID: 25654559
- PMCID: PMC4367445
- DOI: 10.1021/ac504725r
Characterizing sialic acid variants at the glycopeptide level
Abstract
Beam-type collision-induced dissociation (CID) data of intact glycopeptides isolated from mouse liver tissue are presented to illustrate characteristic fragmentation of differentially sialylated glycopeptides. Eight glycoforms of an O-linked glycopeptide from Nucleobindin-1 are distinguished on the basis of the precursor masses and characteristic oxonium ions. We report that all sialic acid variants are prone to neutral loss from the charge reduced species in electron-transfer dissociation (ETD) fragmentation. We show how changes in sialic acid composition affect reverse phase chromatographic retention times: sialic acid addition increases glycopeptide retention times significantly; replacing the N-acetylneuraminic acid with the N-glycolyl variant leads to slightly reduced retention times, while O-acetylated sialic acid-containing glycoforms are retained longer. We then demonstrate how MS-Filter in Protein Prospector can use these diagnostic oxonium ions to find glycopeptides, by showing that a wealth of different glycopeptides can be found in a published phosphopeptide data set.
Figures
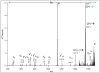

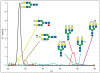
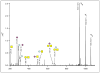
References
-
- Apweiler R, Hermjakob H, Sharon N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:4–8. - PubMed
-
- Jacob GS, Welply JK, Scudder PR, Kirmaier C, Abbas SZ, Howard SC, Keene JL, Schmuke JJ, Broschat K, Steininger C. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;376:283–290. - PubMed
-
- Woronowicz A, Amith SR, De Vusser K, Laroy W, Contreras R, Basta S, Szewczuk MR. Glycobiology. 2007;17:10–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

