Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence factors involved in subversion of leukocytes and microbial dysbiosis
- PMID: 25654623
- PMCID: PMC4601496
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2014.999567
Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence factors involved in subversion of leukocytes and microbial dysbiosis
Abstract
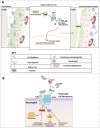
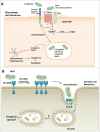
The oral bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis has special nutrient requirements due to its asaccharolytic nature subsisting on small peptides cleaved from host proteins. Using proteases and other virulence factors, P. gingivalis thrives as a component of a polymicrobial community in nutritionally favorable inflammatory environments. In this regard, P. gingivalis has a number of strategies that subvert the host immune response in ways that promote its colonization and facilitate the outgrowth of the surrounding microbial community. The focus of this review is to discuss at the molecular level how P. gingivalis subverts leukocytes to create a favorable environment for a select community of bacteria that, in turn, adversely affects the periodontal tissues.
Keywords: P. gingivalis; dysbiosis; immune subversion; inflammation leukocytes; periodontitis.
Figures
References
-
- Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005; 366:1809-20; PMID:16298220; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67728-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hajishengallis G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15(1):30-44; PMID:25534621; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri3785 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abusleme L, Dupuy AK, Dutzan N, Silva N, Burleson JA, Strausbaugh LD, Gamonal J, Diaz PI. The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. ISME J 2013; 7:1016-25; PMID:23303375; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.174 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jorth P, Turner KH, Gumus P, Nizam N, Buduneli N, Whiteley M. Metatranscriptomics of the human oral microbiome during health and disease. MBio 2014; 5:e01012-14; PMID:24692635; http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01012-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hajishengallis G, Lamont RJ. Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: The Polymicrobial Synergy and Dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Mol Oral Microbiol 2012; 27:409-19; PMID:23134607; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00663.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
