Qualitative and quantitative analysis of MR imaging findings in patients with middle cerebral artery stroke implanted with mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 25655873
- PMCID: PMC8013029
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A4232
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of MR imaging findings in patients with middle cerebral artery stroke implanted with mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Mesenchymal stem cells have potential as a regenerative therapy in ischemic stroke. We sought to determine MR imaging findings after mesenchymal stem cell implantation in chronic middle cerebral artery infarcts and to compare brain volume changes in patients with mesenchymal stem cells with those in age-matched healthy controls and controls with chronic stable MCA infarcts.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively identified 5 patients receiving surgical mesenchymal stem cell implantation to an MCA infarct from January 1, 2005, to July 1, 2013, with MR imaging immediately and 1 year postimplantation. Images at both time points were evaluated for any postimplantation complications. Structural image evaluation using normalization of atrophy software was used to determine volume changes between time points and compare them with those in healthy and age- and sex-matched controls with chronic, stable MCA infarcts by using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests.
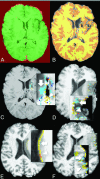
Results: Susceptibility signal loss and enhancement at the implantation site were seen. No teratoma, tumor, or heterotopia was identified. Volumetric analysis showed a trend toward less overall volume loss after mesenchymal stem cell implantation (0.736; 95% CI, -4.15-5.62) compared with that in age- and sex-matched controls with chronic, stable MCA infarcts (-3.59; 95% CI, -12.3 to -5.21; P = .09), with a significantly greater growth-to-loss ratio in infarcted regions (1.30 and 0.78, respectively, P = .02). A trend toward correlation of growth-to-loss ratio with improvement in physical examination findings was seen (r = 0.856, P = .06).
Conclusions: Postoperative changes consistent with stereotactic implantation were seen, but no teratoma, tumor, or heterotopia was identified. Initial findings suggest a trend toward less volume loss after mesenchymal stem cell implantation compared with that in age- and sex-matched controls with chronic, stable MCA infarcts, with a significantly greater growth-to-loss ratio in the infarcted tissue.
© 2015 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures

References
-
- Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, et al. ; for the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics: 2012 update—a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012;125:e2–220
-
- Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD. Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:345–54 - PubMed
-
- Friedrich MA, Martins MP, Araújo MD, et al. Intra-arterial infusion of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in patients with moderate to severe middle cerebral artery acute ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant 2012;21(suppl 1):S13–21 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
