LEADER 2: baseline calcitonin in 9340 people with type 2 diabetes enrolled in the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome Results (LEADER) trial: preliminary observations
- PMID: 25656058
- PMCID: PMC4405040
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.12444
LEADER 2: baseline calcitonin in 9340 people with type 2 diabetes enrolled in the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome Results (LEADER) trial: preliminary observations
Abstract
Aims: To report preliminary data on baseline serum calcitonin concentrations and associated clinical characteristics in a global population with type 2 diabetes before liraglutide or placebo randomization.
Methods: The ongoing LEADER trial has enrolled 9340 people with type 2 diabetes and at high risk of cardiovascular disease at 410 centres worldwide. People with baseline serum calcitonin ≤ 50 ng/l were randomized to liraglutide once daily or placebo and will be followed for up to 5 years. Serum calcitonin was measured at baseline and will be measured annually thereafter. An independent committee of thyroid experts will oversee calcitonin monitoring throughout the trial and will review all calcitonin concentrations ≥ 20 ng/l.
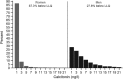
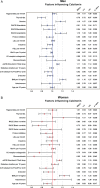
Results: The mean age of participants was 64.3 ± 7.2 years, 64.3% were men, and mean the body mass index was 32.5 ± 6.3 kg/m(2). The median (interquartile range) baseline serum calcitonin values were 3.9 (1.0 to >7.6) ng/l in men and 1.0 (1.0 to >1) ng/l in women. Serum calcitonin was >10 ng/l in 14.6% of men and in 0.96% of women. In sex-specific multivariable linear analysis of covariance models, a reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was associated with higher serum calcitonin concentrations that were statistically significant. A 20 ml/min/1.73 m(2) decrease in estimated GFR (eGFR) was associated with a 14% increase in serum calcitonin in women and an 11% increase in men.
Conclusions: In the LEADER population, the prevalence of elevated serum calcitonin concentrations at baseline was high, and there was an inverse association between eGFR and serum calcitonin concentrations.
Keywords: c-cell disease; calcitonin; diabetes; incretins.
© 2015 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by JohnWiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Garber A, Henry R, Ratner R. Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): a randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment trial. Lancet. 2009;373:473–481. et al. - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Rosenstock J, Sesti G. Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6) Lancet. 2009;374:39–47. et al. - PubMed
-
- Bjerre Knudsen L, Madsen LW, Andersen S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology. 2010;151:1473–1486. et al. - PubMed
-
- Hegedus L, Moses AC, Zdravkovic M, Le Thi T, Daniels GH. GLP-1 and calcitonin concentration in humans: lack of evidence of calcitonin release from sequential screening in over 5000 subjects with type 2 diabetes or nondiabetic obese subjects treated with the human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:853–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

