LRP5 deficiency down-regulates Wnt signalling and promotes aortic lipid infiltration in hypercholesterolaemic mice
- PMID: 25656427
- PMCID: PMC4395191
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12396
LRP5 deficiency down-regulates Wnt signalling and promotes aortic lipid infiltration in hypercholesterolaemic mice
Abstract
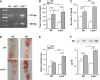
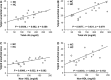
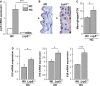
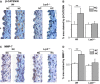
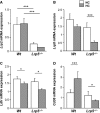
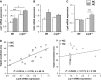
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) is a member of the LDLR family that orchestrates cholesterol homoeostasis. The role of LRP5 and the canonical Wnt pathway in the vascular wall of dyslipidaemic animals remains unknown. In this study, we analysed the role of LRP5 and the Wnt signalling pathway in mice fed a hypercholesterolaemic diet (HC) to trigger dyslipidaemia. We show that Lrp5(-/-) mice had larger aortic lipid infiltrations than wild-type mice, indicating a protective role for LRP5 in the vascular wall. Three members of the LDLR family, Lrp1, Vldlr and Lrp6, showed up-regulated gene expression levels in aortas of Lrp5(-/-) mice fed a hypercholesterolaemic diet. HC feeding in Lrp5(-/-) mice induced higher macrophage infiltration in the aortas and accumulation of inflammatory cytokines in blood. Wnt/β-CATENIN signalling proteins were down-regulated in HC Lrp5(-/-) mice indicating that LRP5 regulates the activation of Wnt signalling in the vascular wall. In conclusion, our findings show that LRP5 and the canonical Wnt pathway down-regulation regulate the dyslipidaemic profile by promoting lipid and macrophage retention in the vessel wall and increasing leucocyte-driven systemic inflammation.
Keywords: LRP5; atherosclerosis; canonical Wnt signalling; macrophages; plasma cholesterol.
© 2015 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LRP5 and plasma cholesterol levels modulate the canonical Wnt pathway in peripheral blood leukocytes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Aug;93(7):653-61. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.41. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25748163
-
Cholesterol modulates LRP5 expression in the vessel wall.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Aug;235(2):363-70. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.05.922. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 24929284
-
Opposing Roles of Wnt Inhibitors IGFBP-4 and Dkk1 in Cardiac Ischemia by Differential Targeting of LRP5/6 and β-catenin.Circulation. 2016 Dec 13;134(24):1991-2007. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024441. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27803037
-
LRPs in WNT Signalling.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;269:45-73. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_526. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34490514 Review.
-
Parameters of LRP5 from a structural and molecular perspective.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2005;15(3):229-42. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v15.i3.50. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2005. PMID: 16390319 Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand trap for the activin type IIA receptor protects against vascular disease and renal fibrosis in mice with chronic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2016 Jun;89(6):1231-43. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27165838 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3β inhibition and canonical Wnt signaling in mice hearts after myocardial ischemic damage.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 20;14(6):e0218098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218098. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31220102 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of microRNA-494-3p activates Wnt signaling and reduces proinflammatory macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 4;26:1228-1239. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.027. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34853722 Free PMC article.
-
Unique Splicing of Lrp5 in the Brain: A New Player in Neurodevelopment and Brain Maturation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 20;25(12):6763. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126763. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928468 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein receptor signalling in atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Jun 1;116(7):1254-1274. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz338. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31834409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badimon L, Storey RF, Vilahur G. Update on lipids, inflammation and atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2011;105:S34–42. - PubMed
-
- Nissen SE, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P, et al. Statin therapy, LDL cholesterol, C-reactive protein, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:29–38. - PubMed
-
- Badimon L, Vilahur G. LDL-cholesterol versus HDL-cholesterol in the atherosclerotic plaque: inflammatory resolution versus thrombotic chaos. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1254:18–32. - PubMed
-
- Jeon H, Blacklow SC. Structure and physiologic function of the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:535–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

