Inhibition of the prostaglandin EP2 receptor is neuroprotective and accelerates functional recovery in a rat model of organophosphorus induced status epilepticus
- PMID: 25656476
- PMCID: PMC4387070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.017
Inhibition of the prostaglandin EP2 receptor is neuroprotective and accelerates functional recovery in a rat model of organophosphorus induced status epilepticus
Abstract
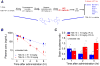
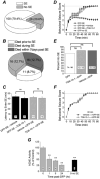
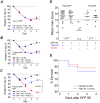
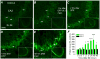
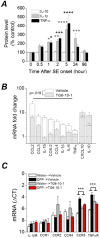
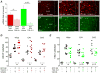
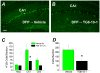
Exposure to high levels of organophosphorus compounds (OP) can induce status epilepticus (SE) in humans and rodents via acute cholinergic toxicity, leading to neurodegeneration and brain inflammation. Currently there is no treatment to combat the neuropathologies associated with OP exposure. We recently demonstrated that inhibition of the EP2 receptor for PGE2 reduces neuronal injury in mice following pilocarpine-induced SE. Here, we investigated the therapeutic effects of an EP2 inhibitor (TG6-10-1) in a rat model of SE using diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP). We tested the hypothesis that EP2 receptor inhibition initiated well after the onset of DFP-induced SE reduces the associated neuropathologies. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with pyridostigmine bromide (0.1 mg/kg, sc) and atropine methylbromide (20 mg/kg, sc) followed by DFP (9.5 mg/kg, ip) to induce SE. DFP administration resulted in prolonged upregulation of COX-2. The rats were administered TG6-10-1 or vehicle (ip) at various time points relative to DFP exposure. Treatment with TG6-10-1 or vehicle did not alter the observed behavioral seizures, however six doses of TG6-10-1 starting 80-150 min after the onset of DFP-induced SE significantly reduced neurodegeneration in the hippocampus, blunted the inflammatory cytokine burst, reduced microglial activation and decreased weight loss in the days after status epilepticus. By contrast, astrogliosis was unaffected by EP2 inhibition 4 d after DFP. Transient treatments with the EP2 antagonist 1 h before DFP, or beginning 4 h after DFP, were ineffective. Delayed mortality, which was low (10%) after DFP, was unaffected by TG6-10-1. Thus, selective inhibition of the EP2 receptor within a time window that coincides with the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by DFP is neuroprotective and accelerates functional recovery of rats.
Keywords: COX-2; DFP; EP2; Hippocampus; Inflammation; Neurodegeneration; Organophosphorus; PGE2; Status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rat model of organophosphate-induced status epilepticus and the beneficial effects of EP2 receptor inhibition.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104399. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30818067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistent behavior deficits, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in a rat model of acute organophosphate intoxication.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104431. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30905768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 prevents status epilepticus-induced deficits in the novel object recognition task in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Nov;110(Pt A):419-430. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.028. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27477533 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Second-Generation EP2 Receptor Antagonist Reduces Neuroinflammation and Gliosis After Status Epilepticus in Rats.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Apr;18(2):1207-1225. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00969-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33410110 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the prostaglandin receptor EP2 following status epilepticus reduces delayed mortality and brain inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 26;110(9):3591-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218498110. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23401547 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early treatment with C1 esterase inhibitor improves weight but not memory deficits in a rat model of status epilepticus.Physiol Behav. 2019 Dec 1;212:112705. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112705. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Physiol Behav. 2019. PMID: 31628931 Free PMC article.
-
A rat model of organophosphate-induced status epilepticus and the beneficial effects of EP2 receptor inhibition.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104399. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30818067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention in Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 13;21(22):8573. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228573. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33202963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripherally Restricted, Highly Potent, Selective, Aqueous-Soluble EP2 Antagonist with Anti-Inflammatory Properties.Mol Pharm. 2018 Dec 3;15(12):5809-5817. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00764. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30398879 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent behavior deficits, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in a rat model of acute organophosphate intoxication.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104431. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30905768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bilak M, Wu L, Wang Q, Haughey N, Conant K, St Hillaire C, Andreasson K. PGE2 receptors rescue motor neurons in a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Annals of neurology. 2004;56:240–8. - PubMed
-
- Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R. Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Experimental neurology. 2003;182:21–34. - PubMed
-
- Chapman S, Kadar T, Gilat E. Seizure duration following sarin exposure affects neuro-inflammatory markers in the rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 2006;27:277–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

