Application of sigma metrics for the assessment of quality control in clinical chemistry laboratory in Ghana: A pilot study
- PMID: 25657495
- PMCID: PMC4314861
- DOI: 10.4103/0300-1652.149172
Application of sigma metrics for the assessment of quality control in clinical chemistry laboratory in Ghana: A pilot study
Abstract
Background: Sigma metrics provide a uniquely defined scale with which we can assess the performance of a laboratory. The objective of this study was to assess the internal quality control (QC) in the clinical chemistry laboratory of the University of Cape Cost Hospital (UCC) using the six sigma metrics application.
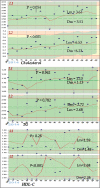
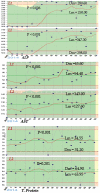
Materials and methods: We used commercial control serum [normal (L1) and pathological (L2)] for validation of quality control. Metabolites (glucose, urea, and creatinine), lipids [triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)], enzymes [alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (AST)], electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride) and total protein were assessed. Between-day imprecision (CVs), inaccuracy (Bias) and sigma values were calculated for each control level.
Results: Apart from sodium (2.40%, 3.83%), chloride (2.52% and 2.51%) for both L1 and L2 respectively, and glucose (4.82%), cholesterol (4.86%) for L2, CVs for all other parameters (both L1 and L2) were >5%. Four parameters (HDL-C, urea, creatinine and potassium) achieved sigma levels >1 for both controls. Chloride and sodium achieved sigma levels >1 for L1 but <1 for L2. In contrast, cholesterol, total protein and AST achieved sigma levels <1 for L1 but >1 for L2. Glucose and ALP achieved a sigma level >1 for both control levels whereas TG achieved a sigma level >2 for both control levels.
Conclusion: Unsatisfactory sigma levels (<3) where achieved for all parameters using both control levels, this shows instability and low consistency of results. There is the need for detailed assessment of the analytical procedures and the strengthening of the laboratory control systems in order to achieve effective six sigma levels for the laboratory.
Keywords: Imprecision; inaccuracy; quality control; six sigma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Westgard JO, Barry PL. Beyond quality assurance: Committing to quality improvement. LabMed; 1989;20:241–7.
-
- Westgard JO, Westgard SA. The quality of laboratory testing today: An assessment of sigma metrics for analytic quality using performance data from proficiency testing surveys and the CLIA criteria for acceptable performance. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125:343–54. - PubMed
-
- Kim YK, Song KE, Lee WK. Reducing patient waiting time for the outpatient phlebotomy service using six sigma. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29:171–7. - PubMed
-
- Plebani M. Exploring the iceberg of errors in laboratory medicine. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;404:16–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

