Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus modulates its membrane lipids in response to hydrogen and nutrient availability
- PMID: 25657645
- PMCID: PMC4302986
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00005
Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus modulates its membrane lipids in response to hydrogen and nutrient availability
Abstract
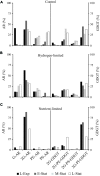
Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus strain ΔH is a model hydrogenotrophic methanogen, for which extensive biochemical information, including the complete genome sequence, is available. Nevertheless, at the cell membrane lipid level, little is known about the responses of this archaeon to environmental stimuli. In this study, the lipid composition of M. thermautotrophicus was characterized to verify how this archaeon modulates its cell membrane components during growth phases and in response to hydrogen depletion and nutrient limitation (potassium and phosphate). As opposed to the higher abundance of phospholipids in the stationary phase of control experiments, cell membranes under nutrient, and energy stress were dominated by glycolipids that likely provided a more effective barrier against ion leakage. We also identified particular lipid regulatory mechanisms in M. thermautotrophicus, which included the accumulation of polyprenols under hydrogen-limited conditions and an increased content of sodiated adducts of lipids in nutrient-limited cells. These findings suggest that M. thermautotrophicus intensely modulates its cell membrane lipid composition to cope with energy and nutrient availability in dynamic environments.
Keywords: archaea; diether; polar lipids; stress response; tetraether.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Targeted Deletion of Genes Responsible for Expression of the Mth60 Fimbriae Leads to Loss of Cell-Cell Connections in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus ΔH.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0057523. doi: 10.1128/aem.00575-23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37310347 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of responses of Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus to different environmental stimuli.Environ Microbiol. 2008 Apr;10(4):893-905. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01508.x. Epub 2007 Nov 25. Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18036179
-
A Shuttle-Vector System Allows Heterologous Gene Expression in the Thermophilic Methanogen Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus ΔH.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0276621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02766-21. Epub 2021 Nov 23. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34809461 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular and Planar Membranes of Archaea Lipids: Unusual Physical Properties and Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 9;23(14):7616. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147616. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures of archaebacterial membrane lipids.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Dec;24(6):555-66. doi: 10.1007/BF00762348. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992. PMID: 1459987 Review.
Cited by
-
Certain, but Not All, Tetraether Lipids from the Thermoacidophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius Can Form Black Lipid Membranes with Remarkable Stability and Exhibiting Mthk Channel Activity with Unusually High Ca2+ Sensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12941. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312941. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884746 Free PMC article.
-
Photosynthesis: Genetic Strategies Adopted to Gain Higher Efficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 16;25(16):8933. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168933. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced methane production from cellulose using a two-stage process involving a bioelectrochemical system and a fixed film reactor.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Jan 6;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01866-x. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 33407783 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Lipid Composition and Amino Acid Excretion Patterns of Methanothermococcus okinawensis Grown in the Presence of Inhibitors Detected in the Enceladian Plume.Life (Basel). 2019 Nov 14;9(4):85. doi: 10.3390/life9040085. Life (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31739502 Free PMC article.
-
The Targeted Deletion of Genes Responsible for Expression of the Mth60 Fimbriae Leads to Loss of Cell-Cell Connections in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus ΔH.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0057523. doi: 10.1128/aem.00575-23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37310347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker K. W., Lipp J. S., Zhu C., Liu X.-L., Hinrichs K.-U. (2013). An improved method for the analysis of archaeal and bacterial ether core lipids. Org. Geochem. 61 34–44 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.05.007 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

