Impulse magnetic stimulation facilitates synaptic regeneration in rats following sciatic nerve injury
- PMID: 25657659
- PMCID: PMC4308799
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.17.003
Impulse magnetic stimulation facilitates synaptic regeneration in rats following sciatic nerve injury
Abstract
The current studies describing magnetic stimulation for treatment of nervous system diseases mainly focus on transcranial magnetic stimulation and rarely focus on spinal cord magnetic stimulation. Spinal cord magnetic stimulation has been confirmed to promote neural plasticity after injuries of spinal cord, brain and peripheral nerve. To evaluate the effects of impulse magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord on peripheral nerve regneration, we compressed a 3 mm segment located in the middle third of the hip using a sterilized artery forceps to induce ischemia. Then, all animals underwent impulse magnetic stimulation of the lumbar portion of spinal crod and spinal nerve roots daily for 1 month. Electron microscopy results showed that in and below the injuryed segment, the inflammation and demyelination of neural tissue were alleviated, apoptotic cells were reduced, and injured Schwann cells and myelin fibers were repaired. These findings suggest that high-frequency impulse magnetic stimulation of spinal cord and corresponding spinal nerve roots promotes synaptic regeneration following sciatic nerve injury.
Keywords: experimental neuropathy; impulse magnetic stimulation; neural regeneration; neuroplasticity; sciatic nerve lesion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
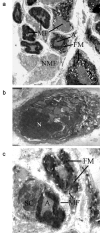
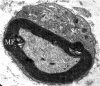

References
-
- Rashidov NA. SPb: MMA; 2001. Evaluation of clinical and electrophysiological effectiveness of come conservative methods in treatment of traumatic neuropathies.
-
- Zhivolupov SA. SPb: MMA; 2000. Traumatic neuropathies and plexopathies (pathogenesis, clinics, diagnostics and treatment)
-
- Zhivolupov SA, Samartsev IN. Neuroplasticity: pathophysiological patterns and perspectives of therapeutic modulation. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2009;109(4):78–84.
-
- Min Y, Beom J, Oh BM, et al. Possible effect of repetitive magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord on the limb angiogenesis in healthy rats and its clinical implication for the treatment of lymphedema. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:47.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
