The cumulative analgesic effect of repeated electroacupuncture involves synaptic remodeling in the hippocampal CA3 region
- PMID: 25657670
- PMCID: PMC4308787
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.18.003
The cumulative analgesic effect of repeated electroacupuncture involves synaptic remodeling in the hippocampal CA3 region
Abstract
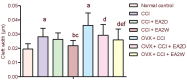
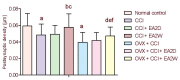
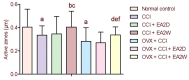
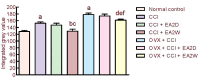
In the present study, we examined the analgesic effect of repeated electroacupuncture at bilateral Zusanli (ST36) and Yanglingquan (GB34) once a day for 14 consecutive days in a rat model of chronic sciatic nerve constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain. In addition, concomitant changes in calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression and synaptic ultrastructure of neurons in the hippocampal CA3 region were examined. The thermal pain threshold (paw withdrawal latency) was increased significantly in both groups at 2 weeks after electroacupuncture intervention compared with 2 days of electroacupuncture. In ovariectomized rats with chronic constriction injury, the analgesic effect was significantly reduced. Electroacupuncture for 2 weeks significantly diminished the injury-induced increase in synaptic cleft width and thinning of the postsynaptic density, and it significantly suppressed the down-regulation of intracellular calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression in the hippocampal CA3 region. Repeated electroacupuncture intervention had a cumulative analgesic effect on injury-induced neuropathic pain reactions, and it led to synaptic remodeling of hippocampal neurons and upregulated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression in the hippocampal CA3 region.
Keywords: acupuncture analgesia; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; chronic neuropathic pain; cumulative effect; electroacupuncture; hippocampal CA3 region; neural regeneration; neurobiology; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Panigada T, Gosselin RD. Behavioural alteration in chronic pain: Are brain glia involved? Med Hypotheses. 2011;77(4):584–588. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS, Magarinos AM. Stress and hippocampal plasticity: implications for the pathophysiology of affective disorders. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2001;16(S1):S7–S19. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS. Plasticity of the hippocampus: adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;933:265–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
