Three-dimensional pharmacophore screening for fentanyl derivatives
- PMID: 25657673
- PMCID: PMC4308790
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.18.006
Three-dimensional pharmacophore screening for fentanyl derivatives
Abstract
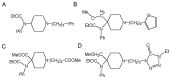
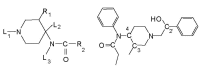
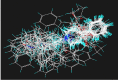
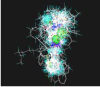
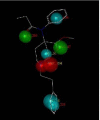
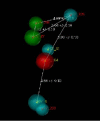
Fentanyl is a highly selective μ-opioid receptor agonist with high analgesic activity. Three-dimensional pharmacophore models were built from a set of 50 fentanyl derivatives. These were employed to elucidate ligand-receptor interactions using information derived only from the ligand structure to identify new potential lead compounds. The present studies demonstrated that three hydrophobic regions, one positive ionizable region and two hydrogen bond acceptor region sites located on the molecule seem to be essential for analgesic activity. The results of the comparative molecular field analysis model suggested that both steric and electrostatic interactions play important roles. The contributions from steric and electrostatic fields for the model were 0.621 and 0.379, respectively. The pharmacophore model provides crucial information about how well the common features of a subject molecule overlap with the hypothesis model, which is very valuable for designing and optimizing new active structures.
Keywords: analgesic; comparative molecular field analysis; fentanyl; genetic algorithm with linear assignment of hypermolecular alignment of datasets; pharmacophore.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening and 3D-QSAR studies of 5-tetrahydroquinolinylidine aminoguanidine derivatives as sodium hydrogen exchanger inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jun 1;22(11):3758-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.012. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22546667
-
Molecular modeling of mu opioid receptor and receptor-ligand interaction.Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1997 Jul;18(4):317-22. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1997. PMID: 10072913
-
Combined pharmacophore modeling, 3D-QSAR, homology modeling and docking studies on CYP11B1 inhibitors.Molecules. 2015 Jan 9;20(1):1014-30. doi: 10.3390/molecules20011014. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25584832 Free PMC article.
-
3D-pharmacophore identification for kappa-opioid agonists using ligand-based drug-design techniques.Top Curr Chem. 2011;299:277-307. doi: 10.1007/128_2010_84. Top Curr Chem. 2011. PMID: 21630511 Review.
-
Conformational landscape of selective mu-opioid agonists in gas phase and in aqueous solution: the fentanyl series.Drug Des Discov. 2000;17(1):55-67. Drug Des Discov. 2000. PMID: 10928449 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization binding studies of opioid receptors, saturation and competition, using [3H]-DAMGO.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Oct;73(5):1390-1395. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00265-9. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33871815
-
Pharmacophore modeling, docking and molecular dynamics to identify Leishmania major farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase inhibitors.J Mol Model. 2018 Oct 16;24(11):314. doi: 10.1007/s00894-018-3838-x. J Mol Model. 2018. PMID: 30327889
References
-
- Li B, Liu M, Hu WX. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations of fentanyl analogs binding to μ-opioid receptors. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao. 2010;26(1):206–214.
-
- Liu M, Li B, Hu WX. 3D QSAR of Imidazoline-derived α (2A)-adrenergic ligands on the basis of molecular docking. Huaxue Tongbao. 2010;(11):989–994.
-
- Hu WX, Li PR, Jiang GX, et al. A mild catalytic oxidation system: alkenes were selectively converted into epoxides, aldehydes, dialcohols and acids catalyzed by ruthenium porphyrin. Adv Synth Catal. 2010;352:3190–3194.
-
- Zhu HW, Fang H, Hu WX, et al. 3D-QSAR study with pharmacophore-based molecular alignment of hydroxamic acid-related phosphinates that are amino-peptidase N inhibitors. Drug Discov T. 2008;2:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Lemmen C, Zimmermann M, Lengauer T. Multiple molecular superpositioning as an effective tool for virtual database screening. Perspect Drug Dis Des. 2000;20(1):43–62.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
