L-tyrosine improves neuroendocrine function in a mouse model of chronic stress
- PMID: 25657675
- PMCID: PMC4308793
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.18.008
L-tyrosine improves neuroendocrine function in a mouse model of chronic stress
Abstract
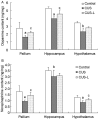
Adult BALB/c mice, individually housed, were stimulated with nine different stressors, arranged randomly, for 4 continuous weeks to generate an animal model of chronic stress. In chronically stressed mice, spontaneous locomotor activity was significantly decreased, escape latency in the Morris water maze test was prolonged, serum levels of total thyrotropin and total triiodothyronine were significantly decreased, and dopamine and norepinephrine content in the pallium, hippocampus and hypothalamus were significantly reduced. All of these changes were suppressed, to varying degrees, by L-tyrosine supplementation. These findings indicate that the neuroendocrine network plays an important role in chronic stress, and that L-tyrosine supplementation has therapeutic effects.
Keywords: L-tyrosine; chronic unpredictable stress; dopamine; neural regeneration; neuroendocrine network; norepinephrine; total thyrotropin; total triiodothyronine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of neonatal and adult hyperthyroidism on behavior and biosynthetic capacity for norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Sep;198(3):609-18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976. PMID: 978462
-
Dynamic changes of behaviors, dentate gyrus neurogenesis and hippocampal miR-124 expression in rats with depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jun;15(6):1150-1159. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.270414. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31823896 Free PMC article.
-
(+)-Sesamin attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and memory deficits via suppression of neuroinflammation.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Feb;64:61-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30445417
-
[Antidepressant effects of the extract of Dendrobium nobile Lindl on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2017 Apr 25;69(2):159-166. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28435974 Chinese.
-
Agmatine attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anxiety, depression-like behaviours and cognitive impairment by modulating nitrergic signalling pathway.Brain Res. 2017 May 15;1663:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28302445
Cited by
-
The Antidepressant-Like Effect of Lactate in an Animal Model of Menopausal Depression.Biomedicines. 2018 Nov 21;6(4):108. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040108. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 30469388 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Avoids Deterioration of Transport Water Quality, Regulates Plasma Biochemical Indices, Energy Metabolism, and Antioxidant Capacity of Tawny Puffer (Takifugui flavidus) under Transport Stress.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;13(7):474. doi: 10.3390/biology13070474. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056669 Free PMC article.
-
Re-interpretation of the mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a framework of psychosomatic medicine: a real-world study.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Nov 8;22(1):689. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04315-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36348380 Free PMC article.
-
Vanillin improves scopolamine‑induced memory impairment through restoration of ID1 expression in the mouse hippocampus.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):4399-4405. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8401. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328430 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chronic Scopolamine Treatment on Cognitive Impairments and Myelin Basic Protein Expression in the Mouse Hippocampus.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Aug;59(4):579-89. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0780-1. Epub 2016 Jun 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27343058
References
-
- Grewen KM, Anderson BJ, Girdler SS, et al. Warm partner contact is related to lower cardiovascular reactivity. Behav Med. 2003;29(3):123–130. - PubMed
-
- Zhu GJ, Duan YP, Xue QF, et al. Changes of urine and plasam catecholmine of expendition members in antartic environment. Jidi Yanjiu. 1998;10(4):305–309.
-
- Xu C, Zhu G, Xue Q, et al. Effect of the Antarctic environment on hormone levels and mood of Chinese expeditioners. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2003;62(3):255–267. - PubMed
-
- Quan M, Zheng C, Zhang N, et al. Impairments of behavior, information flow between thalamus and cortex, and prefrontal cortical synaptic plasticity in an animal model of depression. Brain Res Bull. 2011;85(3-4):109–116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
