Five-year follow-up of 23 asymmetrical Parkinson's disease patients treated with unilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation
- PMID: 25657677
- PMCID: PMC4308795
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.18.010
Five-year follow-up of 23 asymmetrical Parkinson's disease patients treated with unilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation
Abstract
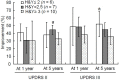
In this study, 23 asymmetrical Parkinson's disease patients were treated with unilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus and followed up for 5 years. At 5 years after stimulation treatment, Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale II, III and axial symptom scores in the off-drug condition were significantly increased compared those at baseline. However, total Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale II, III and axial symptom scores were significantly lower with stimulation-on compared with the synchronous stimulation-off state in off-drug condition, and the motor symptoms of contralateral side limbs were effectively controlled. Only low Hoehn-Yahr stage was correlated with good long-term postoperative improvement in motor symptoms. The mean levodopa-equivalent daily dose after stimulation treatment was significantly lower than that before treatment, but dyskinesias became worse. Our experimental findings indicate that unilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus is an effective treatment for improving motor symptoms in well selected asymmetrical Parkinson's disease patients presenting no severe axial symptoms and dyskinesias.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; deep brain stimulation; neural regeneration; subthalamic nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 .
.
 .
.Similar articles
-
Effect of unilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in highly asymmetrical Parkinson's disease: 7-year follow-up.J Neurosurg. 2018 Nov 23;131(5):1508-1513. doi: 10.3171/2018.5.JNS172006. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30497175
-
Different effectiveness of subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease: A comparative cohort study at 1 year and 5 years.J Formos Med Assoc. 2015 Sep;114(9):835-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Oct 6. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015. PMID: 24103710
-
Parkinson's disease progression at 30 years: a study of subthalamic deep brain-stimulated patients.Brain. 2011 Jul;134(Pt 7):2074-84. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr121. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21666262 Clinical Trial.
-
Subthalamic deep brain stimulation and levodopa in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of combined effects.J Neurol. 2019 Feb;266(2):289-297. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-8936-2. Epub 2018 Jun 16. J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 29909467 Review.
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Patients With Parkinson's Disease: Executive Summary.Neurosurgery. 2018 Jun 1;82(6):753-756. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy037. Neurosurgery. 2018. PMID: 29538685 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influence of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on cognitive function in patients with Parkinson's disease.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Feb;30(1):153-61. doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1389-9. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 24338433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Follow-Up of Unilateral Deep Brain Stimulation Targeting the Caudal Zona Incerta in 13 Patients with Parkinsonian Tremor.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2023;101(6):369-379. doi: 10.1159/000533793. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 37879313 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric neuromodulation of motor circuits in Parkinson's disease: The role of subthalamic deep brain stimulation.Surg Neurol Int. 2017 Oct 24;8:261. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_292_17. eCollection 2017. Surg Neurol Int. 2017. PMID: 29184712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olanow CW, Stern MB, Sethi K. The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease (2009) Neurology. 2009;72(21)(Suppl 4):S1–136. - PubMed
-
- Poewe W. Treatments for Parkinson disease--past achievements and current clinical needs. Neurology. 2009;72(7 Suppl):S65–73. - PubMed
-
- Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Lim SY, et al. The movement disorder society evidence-based medicine review update: Treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2011;26(Suppl 3):S2–41. - PubMed
-
- Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P, et al. Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(16):1105–1111. - PubMed
-
- York MK, Dulay M, Macias A, et al. Cognitive declines following bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(7):789–795. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
