Effect of midazolam on the proliferation of neural stem cells isolated from rat hippocampus
- PMID: 25657682
- PMCID: PMC4308778
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.19.005
Effect of midazolam on the proliferation of neural stem cells isolated from rat hippocampus
Abstract
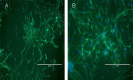
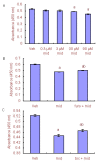
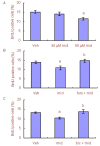
In many recent studies, the inhibitory transmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid has been shown to modulate the proliferation, differentiation and survival of neural stem cells. Most general anesthetics are partial or allosteric gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor agonists, suggesting that general anesthetics could alter the behavior of neural stem cells. The neuroprotective efficacy of general anesthetics has been recognized for decades, but their effects on the proliferation of neural stem cells have received little attention. This study investigated the potential effect of midazolam, an extensively used general anesthetic and allosteric gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor agonist, on the proliferation of neural stem cells in vitro and preliminarily explored the underlying mechanism. The proliferation of neural stem cells was tested using both Cell Counting Kit 8 and bromodeoxyuridine incorporation experiments. Cell distribution analysis was performed to describe changes in the cell cycle distribution in response to midazolam. Calcium imaging was employed to explore the molecular signaling pathways activated by midazolam. Midazolam (30-90 μM) decreased the proliferation of neural stem cells in vitro. Pretreatment with the gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor antagonist bicuculline or Na-K-2Cl cotransport inhibitor furosemide partially rescued this inhibition. In addition, midazolam triggered a calcium influx into neural stem cells. The suppressive effect of midazolam on the proliferation of neural stem cells can be partly attributed to the activation of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor. The calcium influx triggered by midazolam may be a trigger factor leading to further downstream events.
Keywords: gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor; general anesthetics; hippocampus; midazolam; nerve injury; neural regeneration; neural stem cells; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 2008;132(4):645–660. - PubMed
-
- Ge S, Pradhan DA, Ming GL, et al. GABA sets the tempo for activity-dependent adult neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Andang M, Hjerling-Leffler J, Moliner A, et al. Histone H2AX-dependent GABA(A) receptor regulation of stem cell proliferation. Nature. 2008;451(7177):460–464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
