916 MHz electromagnetic field exposure affects rat behavior and hippocampal neuronal discharge
- PMID: 25657684
- PMCID: PMC4308780
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.19.007
916 MHz electromagnetic field exposure affects rat behavior and hippocampal neuronal discharge
Abstract
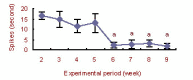
Wistar rats were exposed to a 916 MHz, 10 W/m(2) mobile phone electromagnetic field for 6 hours a day, 5 days a week. Average completion times in an eight-arm radial maze were longer in the exposed rats than control rats after 4-5 weeks of exposure. Error rates in the exposed rats were greater than the control rats at 6 weeks. Hippocampal neurons from the exposed rats showed irregular firing patterns during the experiment, and they exhibited decreased spiking activity 6-9 weeks compared with that after 2-5 weeks of exposure. These results indicate that 916 MHz electromagnetic fields influence learning and memory in rats during exposure, but long-term effects are not obvious.
Keywords: Wistar rats; electromagnetic field; feeding behavior; maze learning; neural regeneration; neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kwon MS, Hamalainen H. Effects of mobile phone electromagnetic fields: critical evaluation of behavioral and neurophysiological studies. Bioelectromagnetics. 2011;32(4):253–272. - PubMed
-
- Bak M, Dudarewicz A, Zmyslony M, et al. Effects of GSM signals during exposure to event related potentials (ERPs) Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2010;23(2):191–199. - PubMed
-
- Curcio G, Nardo D, Perrucci MG, et al. Effects of mobile phone signals over BOLD response while performing a cognitive task. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123(1):129–136. - PubMed
-
- Bas O, Odaci E, Kaplan S, et al. 900 MHz electromagnetic field exposure affects qualitative and quantitative features of hippocampal pyramidal cells in the adult female rat. Brain Res. 2009;1265:178–185. - PubMed
-
- Del Vecchio G, Giuliani A, Fernandez M, et al. Continuous exposure to 900MHz GSM-modulated EMF alters morphological maturation of neural cells. Neurosci Lett. 2009;455(3):173–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
