Dynamic reactive astrocytes after focal ischemia
- PMID: 25657720
- PMCID: PMC4316467
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.147929
Dynamic reactive astrocytes after focal ischemia
Abstract
Astrocytes are specialized and most numerous glial cell type in the central nervous system and play important roles in physiology. Astrocytes are also critically involved in many neural disorders including focal ischemic stroke, a leading cause of brain injury and human death. One of the prominent pathological features of focal ischemic stroke is reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation associated with morphological changes and proliferation. This review paper discusses the recent advances in spatial and temporal dynamics of morphology and proliferation of reactive astrocytes after ischemic stroke based on results from experimental animal studies. As reactive astrocytes exhibit stem cell-like properties, knowledge of dynamics of reactive astrocytes and glial scar formation will provide important insights for astrocyte-based cell therapy in stroke.
Keywords: cell proliferation; cell therapy; dynamics; glial scar; ischemic stroke; morphology; reactive astrocytes.
Figures
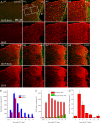
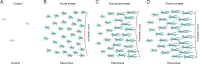
References
-
- Badan I, Buchhold B, Hamm A, Gratz M, Walker LC, Platt D, Kessler C, Popa-Wagner A. Accelerated glial reactivity to stroke in aged rats correlates with reduced functional recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:845–854. - PubMed
-
- Benesova J, Hock M, Butenko O, Prajerova I, Anderova M, Chvatal A. Quantification of astrocyte volume changes during ischemia in situ reveals two populations of astrocytes in the cortex of GFAP/EGFP mice. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87:96–111. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
