Dizziness and Imbalance in the Elderly: Age-related Decline in the Vestibular System
- PMID: 25657851
- PMCID: PMC4306472
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2014.0128
Dizziness and Imbalance in the Elderly: Age-related Decline in the Vestibular System
Abstract
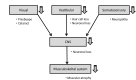
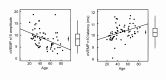
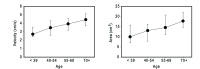
Dizziness and imbalance are amongst the most common complaints in older people, and are a growing public health concern since they put older people at a significantly higher risk of falling. Although the causes of dizziness in older people are multifactorial, peripheral vestibular dysfunction is one of the most frequent causes. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is the most frequent form of vestibular dysfunction in the elderly, followed by Meniere's disease. Every factor associated with the maintenance of postural stability deteriorates during aging. Age-related deterioration of peripheral vestibular function has been demonstrated through quantitative measurements of the vestibulo-ocular reflex with rotational testing and of the vestibulo-collic reflex with testing of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Age-related decline of vestibular function has been shown to correlate with the age-related decrease in the number of vestibular hair cells and neurons. The mechanism of age-related cellular loss in the vestibular endorgan is unclear, but it is thought that genetic predisposition and cumulative effect of oxidative stress may both play an important role. Since the causes of dizziness in older people are multi-factorial, management of this disease should be customized according to the etiologies of each individual. Vestibular rehabilitation is found to be effective in treating both unilateral and bilateral vestibular dysfunction. Various prosthetic devices have also been developed to improve postural balance in older people. Although there have been no medical treatments improving age-related vestibular dysfunction, new medical treatments such as mitochondrial antioxidants or caloric restriction, which have been effective in preventing age-related hearing loss, should be ienvestigated in the future.
Keywords: aging; fall; rehabilitation; vestibular.
Figures
References
-
- Tinetti ME, Williams CS, Gill TM. Dizziness among older adults: a possible geriatric syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(5):337–344. - PubMed
-
- Graafmans WC, Ooms ME, Hofstee HM, Bezemer PD, Bouter LM, Lips P. Falls in the elderly: a prospective study of risk factors and risk profiles. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143(11):1129–1136. - PubMed
-
- Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR. Falls and their prevention in elderly people: what does the evidence show? Med Clin North Am. 2006;90(5):807–824. - PubMed
-
- Stel VS, Pluijm SM, Deeg DJ, Smit JH, Bouter LM, Lips P. A classification tree for predicting recurrent falling in community-dwelling older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(10):1356–1364. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
