Deep brain light stimulation effects on glutamate and dopamine concentration
- PMID: 25657871
- PMCID: PMC4317125
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.6.000023
Deep brain light stimulation effects on glutamate and dopamine concentration
Abstract
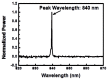
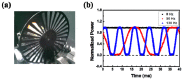
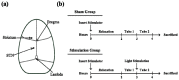
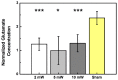
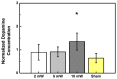
Compared to deep brain electrical stimulation, which has been applied to treating pathological brain diseases, little work has been done on the effect of deep brain light stimulation. A fiber-coupled laser stimulator at 840 nm wavelength and 130 Hz pulse repetition rate is developed in this work for deep brain light stimulation in a rat model. Concentration changes in glutamate and dopamine in the striatum are observed using a microdialysis probe when the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is stimulated at various optical power levels. Experimental results show that light stimulation causes the concentration of glutamate to decrease while that of dopamine is increased. This suggests that deep brain light stimulation of the STN is a promising therapeutic strategy for dopamine-related diseases such as Parkinson's disease. The stimulator developed for this work is useful for deep brain light stimulation in biomedical research.
Keywords: (170.0170) Medical optics and biotechnology; (170.1420) Biology; (170.1610) Clinical applications; (170.3660) Light propagation in tissues; (170.3890) Medical optics instrumentation; (170.5180) Photodynamic therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Sousa F. F. A., Andraus R. A. C., Barbieri C. H., Mazzer N., “Influence of laser radiation in nerve regeneration in different treatment sites,” Acta Ortop. Bras. 17(6), 331–335 (2009).
-
- Ong W.-K., Chen H.-F., Tsai C.-T., Fu Y.-J., Wong Y.-S., Yen D.-J., Chang T.-H., Huang H.-D., Lee O. K., Chien S., Ho J. H., “The activation of directional stem cell motility by green light-emitting diode irradiation,” Biomaterials 34(8), 1911–1920 (2013). 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.11.065 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
