Crystal-induced acute kidney injury due to ciprofloxacin
- PMID: 25657983
- PMCID: PMC4316583
- DOI: 10.12860/jnp.2015.06
Crystal-induced acute kidney injury due to ciprofloxacin
Abstract
Background: Fluoroquinolones are known to cause acute renal failure due to interstitial nephritis.
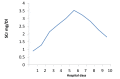
Case presentation: Here we present an elderly woman who developed oliguric acute kidney injury (AKI) after receiving oral and intravenous ciprofloxacin in a 48-hour period. Recently, several case reports have been published in the literature regarding the presence of crystals in the urine sediment of patients treated with ciprofloxacin for different types of systemic infections. Ciprofloxacin crystals precipitate in alkaline urine and provoke renal failure through intra-tubular precipitation.
Conclusions: Conservative measures including intravenous hydration and avoidance of alkalinization of the urine can reverse this condition if applied in time.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Crystalluria; Fluoroquinolones; Interstitial nephritis.
Figures
References
-
- Hottkins R, Fenves AZ, Stephens MK. Acute renal failure secondary to oral ciprofloxacin: A presentation on three cases and a review of the literature. Clin Nephrol. 1989;32:75–8. - PubMed
-
- Ball P. Ciprofloxacin:an overview of adverse experiences. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986;18 Suppl D:187–93. - PubMed
-
- Boll P, Tillotson G. Tolerability of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Drug Safety. 1995;13:344–58. - PubMed
-
- Thorsteinsson SB, Bergan T, Oddsdottir S, Rohwedder R, Holm R. Crystalluria and ciprofloxacin,influence of urinary pH and hydration. Chemotherapy. 1986;32:408–17. - PubMed
-
- Sedlacek M, Suriawinata AA, Schoolwerth A, Remillard BD. Ciprofloxacin crystal nephropathy-A “new” case of acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21(8):2339–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources