Pancreatic Steatosis Demonstrated at MR Imaging in the General Population: Clinical Relevance
- PMID: 25658037
- PMCID: PMC4554208
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.15140446
Pancreatic Steatosis Demonstrated at MR Imaging in the General Population: Clinical Relevance
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the relationship between pancreatic fat content and type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
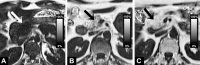
Materials and methods: From the prospective population-based Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP), 1367 volunteers (563 men, 678 women; median age, 50 years) underwent whole-body magnetic resonance (MR) imaging at 1.5 T, which included multiecho chemical shift-encoded acquisition of the abdomen. SHIP was approved by the institutional review board, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The proton density fat fraction (PDFF) was calculated after correction for T1 bias, T2* bias, multipeak spectral complexity of fat, and noise bias. On the basis of oral glucose tolerance test results, participants were grouped into those with normal glucose tolerance (n = 740), those with prediabetes (n = 431), and those with confirmed type 2 diabetes but without medication (n = 70). PDFF was assessed in the pancreatic head, body, and tail. Multivariable regression analysis was conducted to investigate possible relationships of PDFF with demographic factors, behavioral factors, and laboratory data associated with the metabolic syndrome.
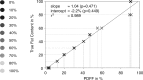
Results: In all subjects, the mean unadjusted pancreatic fat content was 4.4% (head, 4.6%; body, 4.9%; tail, 3.9%; being unequally distributed, P < .001). There was no significant difference in pancreatic PDFF among subjects with normal glucose tolerance, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes (P = .980). Pancreatic PDFF showed a positive association with age and body mass index and a negative association with serum lipase activity (P < .001).
Conclusion: The presence of pancreatic fat is not related to prediabetes or diabetes, which suggests that it has little clinical relevance for an individual's glycemic status.
Figures
References
-
- Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37(12):1595–1607. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome: a new world-wide definition—a consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006;23(5):469–480. - PubMed
-
- van Raalte DH, van der Zijl NJ, Diamant M. Pancreatic steatosis in humans: cause or marker of lipotoxicity? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2010;13(4):478–485. - PubMed
-
- Katz DS, Hines J, Math KR, Nardi PM, Mindelzun RE, Lane MJ. Using CT to reveal fat-containing abnormalities of the pancreas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;172(2):393–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

