Catching the missing million: experiences in enhancing TB & DR-TB detection by providing upfront Xpert MTB/RIF testing for people living with HIV in India
- PMID: 25658091
- PMCID: PMC4319843
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116721
Catching the missing million: experiences in enhancing TB & DR-TB detection by providing upfront Xpert MTB/RIF testing for people living with HIV in India
Abstract
Background: A critical challenge in providing TB care to People Living with HIV (PLHIV) is establishing an accurate bacteriological diagnosis. Xpert MTB/RIF, a highly sensitive and specific rapid tool, offers a promising solution in addressing these challenges. This study presents results from PLHIV taking part in a large demonstration study across India wherein upfront Xpert MTB/RIF testing was offered to all presumptive PTB cases in public health facilities.
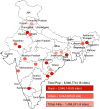
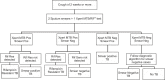
Method: The study covered a population of 8.8 million across 18 sub-district level tuberculosis units (TU), with one Xpert MTB/RIF platform established at each TU. All HIV-infected patients suspected of TB (both TB and Drug Resistant TB (DR-TB)) accessing public health facilities in study area were prospectively enrolled and provided upfront Xpert MTB/RIF testing.
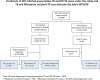
Result: 2,787 HIV-infected presumptive pulmonary TB cases were enrolled and 867 (31.1%, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 29.4‒32.8) HIV-infected TB cases were diagnosed under the study. Overall 27.6% (CI 25.9-29.3) of HIV-infected presumptive PTB cases were positive by Xpert MTB/RIF, compared with 12.9% (CI 11.6-14.1) who had positive sputum smears. Upfront Xpert MTB/RIF testing of presumptive PTB and DR-TB cases resulted in diagnosis of 73 (9.5%, CI 7.6‒11.8) and 16 (11.2%, CI 6.7‒17.1) rifampicin resistance cases, respectively. Positive predictive value (PPV) for rifampicin resistance detection was high 97.7% (CI 89.3‒99.8), with no significant difference with or without prior history of TB treatment.
Conclusion: The study results strongly demonstrate limitations of using smear microscopy for TB diagnosis in PLHIV, leading to low TB and DR-TB detection which can potentially lead to either delayed or sub-optimal TB treatment. Our findings demonstrate the usefulness and feasibility of addressing this diagnostic gap with upfront of Xpert MTB/RIF testing, leading to overall strengthening of care and support package for PLHIV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic (2013) Global report, Page no 4; Available: http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiolo...
-
- TB HIV Facts 2012–2013, Available: http://www.who.int/hiv/topics/tb/tbhiv_facts_2013/en/. Accessed 2014 May 20.
-
- Dewan P, Gupta D, Williams B G, Thakur R, Bachani D, et al. (2010) National estimate of HIV sero prevalence among tuberculosis patients in India. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease; 14(2): 247–9. Available: http://tbcindia.nic.in/pdfs/National%20estimate%20of%20HIV%20seroprevale... - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Global Tuberculosis report (2013), page no 9, Available: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/91355/1/9789241564656_eng.pdf?ua=1
-
- WHO policy on collaborative TB/HIV activities (2012) Guidelines for national programmes and other stakeholders (2012), Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2012/9789241503006_eng.pdf - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

