IL-33/ST2 correlates with severity of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and regulates the inflammatory response in Hantaan virus-infected endothelial cells
- PMID: 25658420
- PMCID: PMC4319827
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003514
IL-33/ST2 correlates with severity of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and regulates the inflammatory response in Hantaan virus-infected endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Hantaan virus (HTNV) causes a severe lethal haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in humans. Despite a limited understanding of the pathogenesis of HFRS, the importance of the abundant production of pro-inflammatory cytokines has been widely recognized. Interleukin 33 (IL-33) has been demonstrated to play an important role in physiological and pathological immune responses. After binding to its receptor ST2L, IL-33 stimulates the Th2-type immune response and promotes cytokine production. Depending on the disease model, IL-33 either protects against infection or exacerbates inflammatory disease, but it is unknown how the IL-33/ST2 axis regulates the immune response during HTNV infection.
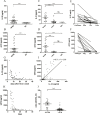
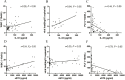
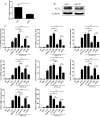
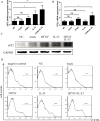
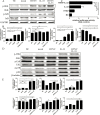
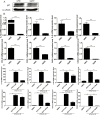
Methodology/principal findings: Blood samples were collected from 23 hospitalized patients and 28 healthy controls. The levels of IL-33 and soluble ST2 (sST2) in plasma were quantified by ELISA, and the relationship between IL-33, sST2 and the disease severity was analyzed. The role of IL-33/sST2 axis in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines was studied on HTNV-infected endothelial cells. The results showed that the plasma IL-33 and sST2 were significantly higher in patients than in healthy controls. Spearman analysis showed that elevated IL-33 and sST2 levels were positively correlated with white blood cell count and viral load, while negatively correlated with platelet count. Furthermore, we found that IL-33 enhanced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in HTNV-infected endothelial cells through NF-κB pathway and that this process was inhibited by the recombinant sST2.
Conclusion/significance: Our results indicate that the IL-33 acts as an initiator of the "cytokine storm" during HTNV infection, while sST2 can inhibit this process. Our findings could provide a promising immunotherapeutic target for the disease control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HTNV-induced upregulation of miR-146a in HUVECs promotes viral infection by modulating pro-inflammatory cytokine release.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Nov 4;493(1):807-813. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.073. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28843856
-
Cytokine response to Hantaan virus infection in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.J Med Virol. 2017 Jul;89(7):1139-1145. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24752. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Med Virol. 2017. PMID: 27943332
-
HTNV Sensitizes Host Toward TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis-A Pivotal Anti-hantaviral Role of TRAIL.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 19;11:1072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01072. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32636833 Free PMC article.
-
Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome: Pathogenesis and Clinical Picture.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Feb 3;6:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00001. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26870699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ST2 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1240:83-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38315-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32060890 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased CD4+CD8+ Double Positive T Cells during Hantaan Virus Infection.Viruses. 2022 Oct 13;14(10):2243. doi: 10.3390/v14102243. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298798 Free PMC article.
-
IL-15 induced bystander activation of CD8+ T cells may mediate endothelium injury through NKG2D in Hantaan virus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 15;12:1084841. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1084841. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36590594 Free PMC article.
-
Superior prognostic value of soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 for the short-term mortality of maintenance hemodialysis patients compared with NT-proBNP: a prospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):523-530. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1767648. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 32460670 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained High Levels of Both Total and High Molecular Weight Adiponectin in Plasma during the Convalescent Phase of Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome Are Associated with Disease Severity.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:6468097. doi: 10.1155/2017/6468097. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28424792 Free PMC article.
-
ST2 contributes to T-cell hyperactivation and fatal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in mice.Blood. 2016 Jan 28;127(4):426-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-659813. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26518437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmaljohn CS, Dalrymple JM (1983) Analysis of Hantaan virus RNA: evidence for a new genus of bunyaviridae. Virology 131: 482–491. - PubMed
-
- Vaheri A, Strandin T, Hepojoki J, Sironen T, Henttonen H, et al. (2013) Uncovering the mysteries of hantavirus infections. Nat Rev Microbiol 11: 539–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

