UFSRAT: Ultra-fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types--the discovery of novel bioactive small molecular scaffolds for FKBP12 and 11βHSD1
- PMID: 25659145
- PMCID: PMC4319890
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116570
UFSRAT: Ultra-fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types--the discovery of novel bioactive small molecular scaffolds for FKBP12 and 11βHSD1
Erratum in
-
Correction: UFSRAT: Ultra-Fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types--the discovery of novel bioactive small molecular scaffolds for FKBP12 and 11βHSD1.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0122658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122658. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25768114 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
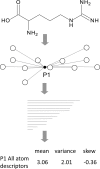
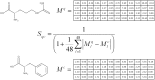
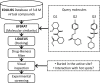
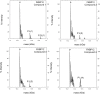
Motivation: Using molecular similarity to discover bioactive small molecules with novel chemical scaffolds can be computationally demanding. We describe Ultra-fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types (UFSRAT), an efficient algorithm that considers both the 3D distribution (shape) and electrostatics of atoms to score and retrieve molecules capable of making similar interactions to those of the supplied query.
Results: Computational optimization and pre-calculation of molecular descriptors enables a query molecule to be run against a database containing 3.8 million molecules and results returned in under 10 seconds on modest hardware. UFSRAT has been used in pipelines to identify bioactive molecules for two clinically relevant drug targets; FK506-Binding Protein 12 and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. In the case of FK506-Binding Protein 12, UFSRAT was used as the first step in a structure-based virtual screening pipeline, yielding many actives, of which the most active shows a KD, app of 281 µM and contains a substructure present in the query compound. Success was also achieved running solely the UFSRAT technique to identify new actives for 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, for which the most active displays an IC50 of 67 nM in a cell based assay and contains a substructure radically different to the query. This demonstrates the valuable ability of the UFSRAT algorithm to perform scaffold hops.
Availability and implementation: A web-based implementation of the algorithm is freely available at http://opus.bch.ed.ac.uk/ufsrat/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correction: UFSRAT: Ultra-Fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types--the discovery of novel bioactive small molecular scaffolds for FKBP12 and 11βHSD1.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0122658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122658. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25768114 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discovery of Potent Inhibitors of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Using a Novel Growth-Based Protocol of in Silico Screening and Optimization in CONTOUR.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Aug 26;59(8):3422-3436. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00198. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31355641
-
Computational prediction of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors from n-butanol fraction of Blighia welwetschii (Hiern) leaf for the management of type-2 diabetes.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024;42(19):10272-10285. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2256869. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37698347
-
Crystal structures of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and their use in drug discovery.Future Med Chem. 2011 Mar;3(3):367-90. doi: 10.4155/fmc.10.282. Future Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21446847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in 11β-HSD1 inhibitors for the treatment of metabolic diseases: A comprehensive guide to their chemical structure diversity in drug development.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Apr 1;191:112134. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112134. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32088493 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: UFSRAT: Ultra-Fast Shape Recognition with Atom Types--the discovery of novel bioactive small molecular scaffolds for FKBP12 and 11βHSD1.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0122658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122658. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25768114 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
USR-VS: a web server for large-scale prospective virtual screening using ultrafast shape recognition techniques.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W436-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw320. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27106057 Free PMC article.
-
Diclofenac Identified as a Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase Binder and Inhibitor by Molecular Similarity Techniques.ACS Omega. 2018 Mar 31;3(3):2564-2568. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b02091. Epub 2018 Mar 2. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30023839 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening applications in short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase research.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Jul;171:157-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28286207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypershape Recognition: A General Framework for Moment-Based Molecular Similarity.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 23;65(12):5960-5972. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00555. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40497694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown RD, Martin YC (1996) Use of Structure-Activity Data To Compare Structure-Based Clustering Methods and Descriptors for Use in Compound Selection. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences 36: 572–584. 10.1021/ci9501047 - DOI
-
- Brown RD, Martin YC (1997) The Information Content of 2D and 3D Structural Descriptors Relevant to Ligand-Receptor Binding. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences 37: 1–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

