Function of the chondrocyte PI-3 kinase-Akt signaling pathway is stimulus dependent
- PMID: 25659655
- PMCID: PMC4444401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.014
Function of the chondrocyte PI-3 kinase-Akt signaling pathway is stimulus dependent
Abstract
Objective: The PI-3 kinase-Akt pathway plays a role in cartilage anabolic as well as catabolic processes in response to activation by insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and oncostatin M (OSM). The goal of this study was to determine how PI-3 kinase-Akt signaling regulates these seemingly opposing functions.
Design: Monolayer cultures of primary human articular chondrocytes were treated with IGF-1, IL-1β, OSM, or the combination of IL-1β and OSM in time course experiments. Activation of signaling proteins and MMP production were measured by immunoblotting. Cells were pre-treated with chemical inhibitors to block mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinases, PI-3 kinase, or JAK/STAT pathway activation. Constitutively active Akt1 and Akt3 were expressed to study stimulus-independent activation of Akt.
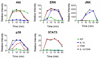
Results: IGF-1, OSM, and the combination of IL-1β and OSM but not IL-1β alone, stimulated phosphorylation of Akt which was sustained longer with IGF-1. IL-1β plus OSM, but not IGF-1, increased chondrocyte MMP-13 production which was inhibited with either a general PI-3 kinase inhibitor or specific inhibition of the PI-3 kinase-γ isoform. Akt1 or Akt3 activity alone was not sufficient to increase production of MMP-13. IL-1β/OSM induced MMP-13 production required activation of the MAP kinases, JNK and p38, as well as the JAK-STAT pathway which were activated by IL-1β plus OSM but not by IGF-1.
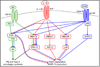
Conclusions: The chondrocyte integrates signals from the PI-3 kinase-Akt pathway with signals from MAP kinases and the JAK-STAT pathway to allow for a differential response to a pro-anabolic (IGF-1) and a pro-catabolic (IL-1β plus OSM) stimulus.
Keywords: Cell signaling; Chondrocyte; Matrix metalloproteinase-13; PI-3 kinase.
Copyright © 2015 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

