PKC δ and βII regulate angiotensin II-mediated fibrosis through p38: a mechanism of RV fibrosis in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 25659900
- PMCID: PMC4398873
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00184.2014
PKC δ and βII regulate angiotensin II-mediated fibrosis through p38: a mechanism of RV fibrosis in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
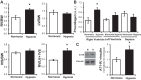
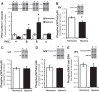
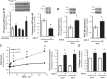
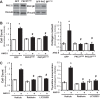
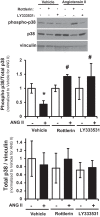
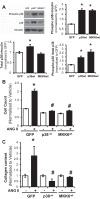
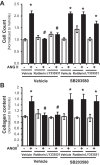
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) eventually leads to right ventricular (RV) fibrosis and dysfunction that is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Although angiotensin II plays an important role in RV remodeling associated with hypoxic PH, the molecular mechanisms underlying RV fibrosis in PH largely remain unresolved. We hypothesized that PKC-p38 signaling is involved in RV collagen accumulation in PH and in response to angiotensin II stimulation. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to 3 wk of normoxia or hypoxia (10% FiO2 ) as a model of PH. Hypoxic rats developed RV hypertrophy and fibrosis associated with an increase in PKC βII and δ protein expression and p38 dephosphorylation in freshly isolated RV cardiac fibroblasts. Further mechanistic studies were performed in cultured primary cardiac fibroblasts stimulated with angiotensin II, a key activator of ventricular fibrosis in PH. Angiotensin II induced a reduction in p38 phosphorylation that was attenuated following chemical inhibition of PKC βII and δ. Molecular and chemical inhibition of PKC βII and δ abrogated angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition in vitro. The effects of PKC inhibition on proliferation and fibrosis were reversed by chemical inhibition of p38. Conversely, constitutive activation of p38 attenuated angiotensin II-induced increase of cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen accumulation. PKC βII- and δ-dependent inactivation of p38 regulates cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition in response to angiotensin II, which suggests that the PKC-p38 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts may be involved and important in the pathophysiology of RV fibrosis in PH.
Keywords: PKC; angiotensin II; cardiac fibroblast; p38; pulmonary hypertension; right ventricle.
Figures
References
-
- Bartha E, Solti I, Kereskai L, Lantos J, Plozer E, Magyar K, Szabados E, Kalai T, Hideg K, Halmosi R, Sumegi B, Toth K. PARP inhibition delays transition of hypertensive cardiopathy to heart failure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res 83: 501–510, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Bogaard HJ, Abe K, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Voelkel NF. The right ventricle under pressure: cellular and molecular mechanisms of right-heart failure in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 135: 794–804, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Booz GW, Baker KM. Protein kinase C in angiotensin II signalling in neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts. Role in the mitogenic response. Ann NY Acad Sci 752: 158–167, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Braun MU, LaRosee P, Simonis G, Borst MM, Strasser RH. Regulation of protein kinase C isozymes in volume overload cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 262: 135–143, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Braz JC, Bueno OF, Liang Q, Wilkins BJ, Dai YS, Parsons S, Braunwart J, Glascock BJ, Klevitsky R, Kimball TF, Hewett TE, Molkentin JD. Targeted inhibition of p38 MAPK promotes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through upregulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling. J Clin Invest 111: 1475–1486, 2003. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

