The Pex1/Pex6 complex is a heterohexameric AAA+ motor with alternating and highly coordinated subunits
- PMID: 25659908
- PMCID: PMC4355278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.01.019
The Pex1/Pex6 complex is a heterohexameric AAA+ motor with alternating and highly coordinated subunits
Abstract
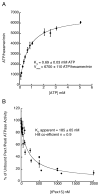
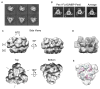
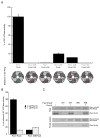
Pex1 and Pex6 are Type-2 AAA+ ATPases required for the de novo biogenesis of peroxisomes. Mutations in Pex1 and Pex6 account for the majority of the most severe forms of peroxisome biogenesis disorders in humans. Here, we show that the ATP-dependent complex of Pex1 and Pex6 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a heterohexamer with alternating subunits. Within the Pex1/Pex6 complex, only the D2 ATPase ring hydrolyzes ATP, while nucleotide binding in the D1 ring promotes complex assembly. ATP hydrolysis by Pex1 is highly coordinated with that of Pex6. Furthermore, Pex15, the membrane anchor required for Pex1/Pex6 recruitment to peroxisomes, inhibits the ATP-hydrolysis activity of Pex1/Pex6.
Keywords: AAA+ ATPase; Pex1; Pex15; Pex6; peroxisome.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Tabak HF, Braakman I, van der Zand A. Peroxisome formation and maintenance are dependent on the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:723–44. - PubMed
-
- Weller S, Gould SJ, Valle D. Peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2003;4:165–211. - PubMed
-
- Schluter A, Fourcade S, Ripp R, Mandel JL, Poch O, Pujol A. The evolutionary origin of peroxisomes: an ER-peroxisome connection. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23:838–45. - PubMed
-
- Hoepfner D, Schildknegt D, Braakman I, Philippsen P, Tabak HF. Contribution of the endoplasmic reticulum to peroxisome formation. Cell. 2005;122:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

