Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 25662011
- PMCID: PMC4498261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.012
Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Impaired insulin-mediated suppression of hepatic glucose production (HGP) plays a major role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2D), yet the molecular mechanism by which this occurs remains unknown. Using a novel in vivo metabolomics approach, we show that the major mechanism by which insulin suppresses HGP is through reductions in hepatic acetyl CoA by suppression of lipolysis in white adipose tissue (WAT) leading to reductions in pyruvate carboxylase flux. This mechanism was confirmed in mice and rats with genetic ablation of insulin signaling and mice lacking adipose triglyceride lipase. Insulin's ability to suppress hepatic acetyl CoA, PC activity, and lipolysis was lost in high-fat-fed rats, a phenomenon reversible by IL-6 neutralization and inducible by IL-6 infusion. Taken together, these data identify WAT-derived hepatic acetyl CoA as the main regulator of HGP by insulin and link it to inflammation-induced hepatic insulin resistance associated with obesity and T2D.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
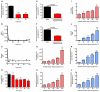
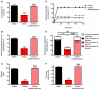
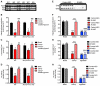
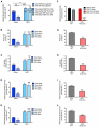
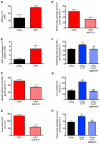
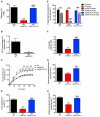
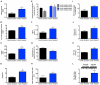
Comment in
-
Metabolism. Hepatic insulin resistance--missing link identified.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;11(4):193. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.17. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25707785 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barritt GJ, Keech DB, Ling AM. Apparent co-operative effect of acetyl-CoA on sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1966;24:476–481. - PubMed
-
- Beylot M, David F, Brunengraber H. Determination of the 13C-labeling pattern of glutamate by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1993;212:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Cartee GD, Bohn EE. Growth hormone reduces glucose transport but not GLUT-1 or GLUT-4 in adult and old rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;268:E902–E909. - PubMed
-
- Cazzulo JJ, Stoppani AO. The regulation of yeast pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl-coenzyme A and L-aspartate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968;127:563–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 DK101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD028016/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089098/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK099402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK-085638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK93928/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-40936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-093959/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-056886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087568/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK-45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK-090963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK085638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK101175/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD028016/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS-087568/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085577/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD 04787/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK-059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093959/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK-101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG-023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093928/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR-000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

