EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA
- PMID: 25662012
- PMCID: PMC4329084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.015
EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA
Abstract
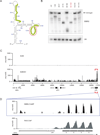
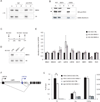
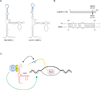
EBER2 is an abundant nuclear noncoding RNA expressed by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Probing its possible chromatin localization by CHART revealed EBER2's presence at the terminal repeats (TRs) of the latent EBV genome, overlapping previously identified binding sites for the B cell transcription factor PAX5. EBER2 interacts with PAX5 and is required for the localization of PAX5 to the TRs. EBER2 knockdown phenocopies PAX5 depletion in upregulating the expression of LMP2A/B and LMP1, genes nearest the TRs. Knockdown of EBER2 also decreases EBV lytic replication, underscoring the essential role of the TRs in viral replication. Recruitment of the EBER2-PAX5 complex is mediated by base-pairing between EBER2 and nascent transcripts from the TR locus. The interaction is evolutionarily conserved in the related primate herpesvirus CeHV15 despite great sequence divergence. Using base-pairing with nascent RNA to guide an interacting transcription factor to its DNA target site is a previously undescribed function for a trans-acting noncoding RNA.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
RNA: jack of all trades and master of all.Cell. 2015 Feb 12;160(4):579-580. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.047. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25679756
Similar articles
-
Identification of host RNAs that interact with EBV noncoding RNA EBER2.RNA Biol. 2018;15(9):1181-1191. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1518854. Epub 2018 Sep 18. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 30176159 Free PMC article.
-
EBV noncoding RNA EBER2 interacts with host RNA-binding proteins to regulate viral gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 22;113(12):3221-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601773113. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26951683 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell-Specific Transcription Activator PAX5 Recruits p300 To Support EBNA1-Driven Transcription.J Virol. 2020 Mar 17;94(7):e02028-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02028-19. Print 2020 Mar 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31941781 Free PMC article.
-
RNA families in Epstein-Barr virus.RNA Biol. 2014;11(1):10-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.27488. Epub 2013 Dec 20. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24441309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus.Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Feb;17(2):81-92. doi: 10.1007/BF00996215. Mol Biol Rep. 1993. PMID: 8384694 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNAs: Re-writing dogmas of RNA processing and stability.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1859(1):128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26073320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles and Practices of Hybridization Capture Experiments to Study Long Noncoding RNAs That Act on Chromatin.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Nov 1;11(11):a032276. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032276. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31676573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of STAT3 in Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Hodgkin Lymphoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 6;10(7):1608. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071608. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884913 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid strand displacement - from DNA nanotechnology to translational regulation.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):154-163. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2204565. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37095744 Free PMC article.
-
RNA matchmaking in chromatin regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2467-2481. doi: 10.1042/BST20191225. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33245317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bulut-Karslioglu A, Perrera V, Scaranaro M, de la Rosa-Velazquez IA, van de Nobelen S, Shukeir N, Popow J, Gerle B, Opravil S, Pagani M, et al. A transcription factor-based mechanism for mouse heterochromatin formation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:1023–1030. - PubMed
-
- Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157:77–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

