Developing and regenerating a sense of taste
- PMID: 25662267
- PMCID: PMC4435577
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.012
Developing and regenerating a sense of taste
Abstract
Taste is one of the fundamental senses, and it is essential for our ability to ingest nutritious substances and to detect and avoid potentially toxic ones. Taste buds, which are clusters of neuroepithelial receptor cells, are housed in highly organized structures called taste papillae in the oral cavity. Whereas the overall structure of the taste periphery is conserved in almost all vertebrates examined to date, the anatomical, histological, and cell biological, as well as potentially the molecular details of taste buds in the oral cavity are diverse across species and even among individuals. In mammals, several types of gustatory papillae reside on the tongue in highly ordered arrangements, and the patterning and distribution of the mature papillae depend on coordinated molecular events in embryogenesis. In this review, we highlight new findings in the field of taste development, including how taste buds are patterned and how taste cell fate is regulated. We discuss whether a specialized taste bud stem cell population exists and how extrinsic signals can define which cell lineages are generated. We also address the question of whether molecular regulation of taste cell renewal is analogous to that of taste bud development. Finally, we conclude with suggestions for future directions, including the potential influence of the maternal diet and maternal health on the sense of taste in utero.
Keywords: Cell lineage; Differentiation; Epithelial; FGF; Gustation; Lingual; Patterning; Placode; Shh; Stem cell; Tongue; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

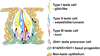
References
-
- Adams AE. Some effects of removal of endoderm from the mouth region of early Amblystoma punctatum embryos. J. exp. Zool. 1931;58:147–163.
-
- Atema J. Structures and functions of the sense of taste in the catfish (Ictalurus natalis) Brain Behav. Evol. 1971;4:273–294. - PubMed
-
- Banziger C, Soldini D, Schutt C, Zipperlen P, Hausmann G, Basler K. Wntless, a conserved membrane protein dedicated to the secretion of Wnt proteins from signaling cells. Cell. 2006;125:509–522. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Tan S, Clevers H. Lgr proteins in epithelial stem cell biology. Development. 2013;140:2484–2494. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

