[Children's eating behaviour: comparison between normal and overweight children from a school in Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil]
- PMID: 25662562
- PMCID: PMC4436955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpped.2014.11.007
[Children's eating behaviour: comparison between normal and overweight children from a school in Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil]
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:: To evaluate differences in children's eating behavior in relation to their nutritional status, gender and age.
METHODS:: Male and female children aged six to ten years were included. They were recruited from a private school in the city of Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil, in 2012. Children´s Eating Behaviour Questionnaire (CEBQ) subscales were used to assess eating behaviors: Food Responsiveness (FR), Enjoyment of Food (EF), Desire to Drink (DD), Emotional Overeating (EOE), Emotional Undereating (EUE), Satiety Responsiveness (SR), Food Fussiness (FF) and Slowness in Eating (SE). Age-adjusted body mass index (BMI) z-scores were calculated according to the WHO recommendations to assess nutritional status.
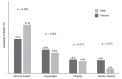
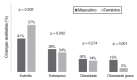
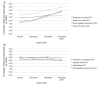
RESULTS:: The study sample comprised 335 children aged 87.9±10.4 months and 49.3% had normal weight (n=163), 26% were overweight (n=86), 15% were obese (n=50) and 9.7% were severely obese (n=32). Children with excess weight showed higher scores at the CEBQ subscales associated with "food approach" (FR, EF, DD, EOE, p<0.001) and lower scores on two "food avoidance" subscales (SR and SE, p<0.001 and p=0.003, respectively) compared to normal weight children. Differences in the eating behavior related to gender and age were not found.
CONCLUSIONS:: "Food approach" subscales were positively associated to excess weight in children, but no associations with gender and age were found.
Keywords: Avaliação nutricional; Child; Comportamento alimentar; Criança; Feeding behavior; Nutritional assessment; Obesidade; Obesity.
Copyright © 2014 Associação de Pediatria de São Paulo. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Examining behavioural susceptibility to obesity among Canadian pre-school children: the role of eating behaviours.Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011 Jun;6(2-2):e501-7. doi: 10.3109/17477166.2010.512087. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011. PMID: 20831463
-
GOCS cohort: children's eating behavior scores and BMI.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016 Aug;70(8):925-8. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.18. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27071512
-
The children's eating behaviour questionnaire: factorial validity and association with Body Mass Index in Dutch children aged 6-7.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2008 Oct 20;5:49. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-5-49. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2008. PMID: 18937832 Free PMC article.
-
The association between childhood adiposity and appetite assessed using the Child Eating Behavior Questionnaire and Baby Eating Behavior Questionnaire: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Obes Rev. 2021 May;22(5):e13169. doi: 10.1111/obr.13169. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Obes Rev. 2021. PMID: 33554425
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Factorial Model of Obese Adolescents: The Role of Body Image Concerns and Selective Depersonalization-A Pilot Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 13;19(18):11501. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811501. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36141782 Free PMC article.
-
Eating Behaviors in Relation to Child Weight Status and Maternal Education.Children (Basel). 2021 Jan 7;8(1):32. doi: 10.3390/children8010032. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33430408 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Eating Behaviour on the Growth of Children from the Interior Districts of Sabah, Malaysia.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2022 Apr 2;15:563-570. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S330358. eCollection 2022. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2022. PMID: 35400133 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Eating Behavior among 13-Year-Old Adolescents and Associated Factors: Findings from the Generation XXI Birth Cohort.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 10;11(10):1371. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11101371. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239660 Free PMC article.
-
Children's eating behaviour: A comparison between normal, overweight and obese children.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Nov 13;84:104890. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104890. eCollection 2022 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36536714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossi A, Moreira EA, Rauen MS. Determinants of eating behavior: a review focusing on the family. Rev Nutr. 2008;21:739–748.
-
- Brasil-Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatísticas Pesquisa de orçamentos familiares 2008-2009. [14 February 2013]. a Available from: http://www.ibge.gov.br.
-
- Wardle J, Guthrie CA, Sanderson S, Rapoport L. Development of the children's eating behaviour questionnaire. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Viana V, Sinde S. O comportamento alimentar em crianças: estudo de validação de um questionário numa amostra portuguesa (CEBQ) Ana Psicologica. 2008;1:111–120.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

