ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease
- PMID: 25664248
- PMCID: PMC4317630
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i1.74
ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease
Abstract
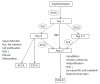
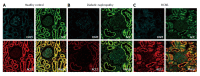
Renin angiotensin system (RAS) activation has a significant influence on renal disease progression. The classical angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-angiotensin II (Ang II)-Ang II type 1 (AT1) axis is considered to control the effects of RAS activation on renal disease. However, since its discovery in 2000 ACE2 has also been demonstrated to have a significant impact on the RAS. The synthesis and catabolism of Ang II are regulated via a complex series of interactions, which involve ACE and ACE2. In the kidneys, ACE2 is expressed in the proximal tubules and less strongly in the glomeruli. The synthesis of inactive Ang 1-9 from Ang I and the catabolism of Ang II to produce Ang 1-7 are the main functions of ACE2. Ang 1-7 reduces vasoconstriction, water retention, salt intake, cell proliferation, and reactive oxygen stress, and also has a renoprotective effect. Thus, in the non-classical RAS the ACE2-Ang 1-7-Mas axis counteracts the ACE-Ang II-AT1 axis. This review examines recent human and animal studies about renal ACE and ACE2.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme; Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Diabetic nephropathy; Kidney disease; Renin angiotensin system.
Figures
References
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33238–33243. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
-
- Santos RA, Ferreira AJ, Verano-Braga T, Bader M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas: new players of the renin-angiotensin system. J Endocrinol. 2013;216:R1–R17. - PubMed
-
- Burns KD. The emerging role of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 in the kidney. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007;16:116–121. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

