Behaviour of four different B16 murine melanoma cell sublines: C57BL/6J skin
- PMID: 25664478
- PMCID: PMC4459798
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12114
Behaviour of four different B16 murine melanoma cell sublines: C57BL/6J skin
Abstract
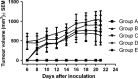
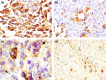
Transplantable murine melanomas are well-established models for the study of experimental cancer therapies. The aim of this study was to explore the behaviour of four different B16 murine melanoma cell sublines after inoculation into C57BL/6J mice; and, more specifically to analyse skin changes, with respect to two specific parameters: clinical (tumour volume, melanin amount, erythema) and histological (H & E, S100, VEGF expression). Both non-invasive and invasive analysis showed that B164A5 is the most aggressive melanoma cell line for C57BL/6J's skin, followed by B16F10 and then by diminished aggressive growth pattern by the B16GMCSF and B16FLT3 cell lines.
Keywords: B164A5; B16F10; B16FLT3; B16GMCSF; C57BL/6J.
© 2015 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2015 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures




References
-
- Andrade P, Brites MM, Vieira R, et al. Epidemiology of basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas in a Department of Dermatology: a 5 year review. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2012;87:212–219. - PubMed
-
- Brenner S. Wolf R. The “red face” – a warning sign of malignant melanoma? Acta Derm. Venereol. 1992;72:464. - PubMed
-
- Brozyna A, VanMiddlesworth L, Slominski AT. Inhibition of melanogenesis as a radiation sensitizer for melanoma therapy. Int. J. Cancer. 2008;123:448–456. - PubMed
-
- Brychtova S, Bezdekova M, Brychta T, Tichy M. The role of vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in malignant melanomas. Neoplasma. 2008;55:273–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

