Tribolium castaneum RR-1 cuticular protein TcCPR4 is required for formation of pore canals in rigid cuticle
- PMID: 25664770
- PMCID: PMC4335487
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004963
Tribolium castaneum RR-1 cuticular protein TcCPR4 is required for formation of pore canals in rigid cuticle
Abstract
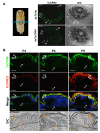
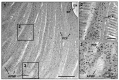
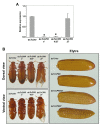
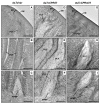
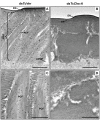
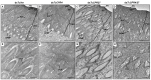
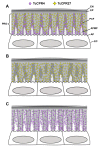
Insect cuticle is composed mainly of structural proteins and the polysaccharide chitin. The CPR family is the largest family of cuticle proteins (CPs), which can be further divided into three subgroups based on the presence of one of the three presumptive chitin-binding sequence motifs denoted as Rebers-Riddiford (R&R) consensus sequence motifs RR-1, RR-2 and RR-3. The TcCPR27 protein containing the RR-2 motif is one of the most abundant CPs present both in the horizontal laminae and in vertical pore canals in the procuticle of rigid cuticle found in the elytron of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Depletion of TcCPR27 by RNA interference (RNAi) causes both unorganized laminae and pore canals, resulting in malformation and weakening of the elytron. In this study, we investigated the function(s) of another CP, TcCPR4, which contains the RR-1 motif and is easily extractable from elytra after RNAi to deplete the level of TcCPR27. Transcript levels of the TcCPR4 gene are dramatically increased in 3 d-old pupae when adult cuticle synthesis begins. Immunohistochemical studies revealed that TcCPR4 protein is present in the rigid cuticles of the dorsal elytron, ventral abdomen and leg but not in the flexible cuticles of the hindwing and dorsal abdomen of adult T. castaneum. Immunogold labeling and transmission electron microscopic analyses revealed that TcCPR4 is predominantly localized in pore canals and regions around the apical plasma membrane protrusions into the procuticle of rigid adult cuticles. RNAi for TcCPR4 resulted in an abnormal shape of the pore canals with amorphous pore canal fibers (PCFs) in their lumen. These results support the hypothesis that TcCPR4 is required for achieving proper morphology of the vertical pore canals and PCFs that contribute to the assembly of a cuticle that is both lightweight and rigid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two major cuticular proteins are required for assembly of horizontal laminae and vertical pore canals in rigid cuticle of Tribolium castaneum.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Oct;53:22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25042128
-
Development and ultrastructure of the rigid dorsal and flexible ventral cuticles of the elytron of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Dec;91:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 5. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 29117500
-
Group I chitin deacetylases are essential for higher order organization of chitin fibers in beetle cuticle.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 4;293(18):6985-6995. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001454. Epub 2018 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29567838 Free PMC article.
-
Cuticle formation and pigmentation in beetles.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016 Oct;17:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 12. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016. PMID: 27720067 Review.
-
Structural cuticular proteins from arthropods: annotation, nomenclature, and sequence characteristics in the genomics era.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Mar;40(3):189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20171281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CPR63 promotes pyrethroid resistance by increasing cuticle thickness in Culex pipiens pallens.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Feb 14;15(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05175-0. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35164827 Free PMC article.
-
Cuticular protein with a low complexity sequence becomes cross-linked during insect cuticle sclerotization and is required for the adult molt.Sci Rep. 2015 May 21;5:10484. doi: 10.1038/srep10484. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25994234 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis and endocuticular protein gene expression of alate adults, workers and soldiers of the termite Reticulitermes aculabialis.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 15;20(1):742. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6149-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31615402 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring integument transcriptomes, cuticle ultrastructure, and cuticular hydrocarbons profiles in eusocial and solitary bee species displaying heterochronic adult cuticle maturation.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 14;14(3):e0213796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213796. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30870522 Free PMC article.
-
A chitinase with two catalytic domains is required for organization of the cuticular extracellular matrix of a beetle.PLoS Genet. 2018 Mar 28;14(3):e1007307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007307. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29590098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Locke M (2001) The Wigglesworth Lecture: Insects for studying fundamental problems in biology. J Insect Physiol 47: 495–507. - PubMed
-
- Moussian B, Seifarth C, Muller U, Berger J, Schwarz H (2006) Cuticle differentiation during Drosophila embryogenesis. Arthropod Struct Dev 35: 137–152. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins TL, Kramer KJ (1992) Insect cuticle sclerotization. Annu Rev Entomol 37: 273–302.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

