Predictors of Progression From the Appearance of Islet Autoantibodies to Early Childhood Diabetes: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY)
- PMID: 25665818
- PMCID: PMC4407751
- DOI: 10.2337/dc14-2426
Predictors of Progression From the Appearance of Islet Autoantibodies to Early Childhood Diabetes: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY)
Abstract
Objective: While it is known that there is progression to diabetes in <10 years in 70% of children with two or more islet autoantibodies, predictors of the progression to diabetes are only partially defined.
Research design and methods: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study has observed 8,503 children who were at increased genetic risk for autoimmune diabetes. Insulin autoantibodies (IAAs), GAD65 autoantibodies (GADAs), and insulinoma-associated protein 2 autoantibodies (IA-2As) were measured every 3 months until 4 years of age and every 6 months thereafter; if results were positive, the autoantibodies were measured every 3 months.
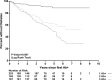
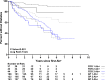
Results: Life table analysis revealed that the cumulative incidence of diabetes by 5 years since the appearance of the first autoantibody differed significantly by the number of positive autoantibodies (47%, 36%, and 11%, respectively, in those with three autoantibodies, two autoantibodies, and one autoantibody, P < 0.001). In time-varying survival models adjusted for first-degree relative status, number of autoantibodies, age at first persistent confirmed autoantibodies, and HLA genotypes, higher mean IAA and IA-2A levels were associated with an increased risk of type 1 diabetes in children who were persistently autoantibody positive (IAAs: hazard ratio [HR] 8.1 [95% CI 4.6-14.2]; IA-2A: HR 7.4 [95% CI 4.3-12.6]; P < 0.0001]). The mean GADA level did not significantly affect the risk of diabetes.
Conclusions: In the TEDDY study, children who have progressed to diabetes usually expressed two or more autoantibodies. Higher IAA and IA-2A levels, but not GADA levels, increased the risk of diabetes in those children who were persistently autoantibody positive.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
References
-
- Palmer JP, Asplin CM, Clemons P, et al. . Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science 1983;222:1337–1339 - PubMed
-
- Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot H-J, Christgau S, et al. . Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature 1990;347:151–156 - PubMed
-
- Gianani R, Rabin DU, Verge CF, et al. . ICA512 autoantibody radioassay. Diabetes 1995;44:1340–1344 - PubMed
-
- Bingley PJ, Bonifacio E, Ziegler AG, Schatz DA, Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS; Immunology of Diabetes Society . Proposed guidelines on screening for risk of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24:398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-95300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials