Systolic Blood Pressure Control Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparative Effectiveness Analysis of Three Interventions
- PMID: 25666468
- PMCID: PMC4506323
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpu292
Systolic Blood Pressure Control Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparative Effectiveness Analysis of Three Interventions
Abstract
Background: The relative effectiveness of 3 approaches to blood pressure control-(i) an intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) focused on weight loss, (ii) frequent goal-based monitoring of blood pressure with pharmacological management, and (iii) education and support-has not been established among overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes who are appropriate for each intervention.
Methods: Participants from the Action for Health in Diabetes (Look AHEAD) and the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) cohorts who met criteria for both clinical trials were identified. The proportions of these individuals with systolic blood pressure (SBP) <140 mm Hg from annual standardized assessments over time were compared with generalized estimating equations.
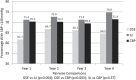
Results: Across 4 years among 480 Look AHEAD and 1,129 ACCORD participants with baseline SBPs between 130 and 159 mm Hg, ILI (OR = 1.46; 95% CI = [1.18-1.81]) and frequent goal-based monitoring with pharmacotherapy (OR = 1.51; 95% CI = [1.16-1.97]) yielded higher rates of blood pressure control compared to education and support. The intensive behavioral-based intervention may have been more effective among individuals with body mass index >30 kg/m2, while frequent goal-based monitoring with medication management may be more effective among individuals with lower body mass index (interaction P = 0.047).
Conclusions: Among overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes, both ILI and frequent goal-based monitoring with pharmacological management can be successful strategies for blood pressure control.
Clinical trials registry: clinicaltrials.gov identifiers NCT00017953 (Look AHEAD) and NCT00000620 (ACCORD).
Keywords: blood pressure; blood pressure control; blood pressure monitoring; comparative effectiveness; diabetes; hypertension; lifestyle intervention; obesity..
© American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd 2015. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Li C, Balluz LS, Ford ES, Okoro CA, Zhao G, Pierannunzi C. A comparison of prevalence estimates for selected health indicators and chronic disease conditions from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, the National Health Interview Survey, and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2008. Prev Med 2012; 54:281–387. - PubMed
-
- The Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The sixth report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Arch Intern Med 1997; 157:2413–2446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Y1-HC-9035/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK098722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95183/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95179/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000170/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95180/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007244/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001120/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Y1-HC-1010/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95178/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95181/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95182/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95184/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

