RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes
- PMID: 25666585
- PMCID: PMC4322359
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08365
RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes
Abstract
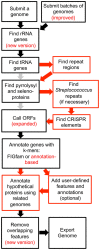
The RAST (Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology) annotation engine was built in 2008 to annotate bacterial and archaeal genomes. It works by offering a standard software pipeline for identifying genomic features (i.e., protein-encoding genes and RNA) and annotating their functions. Recently, in order to make RAST a more useful research tool and to keep pace with advancements in bioinformatics, it has become desirable to build a version of RAST that is both customizable and extensible. In this paper, we describe the RAST tool kit (RASTtk), a modular version of RAST that enables researchers to build custom annotation pipelines. RASTtk offers a choice of software for identifying and annotating genomic features as well as the ability to add custom features to an annotation job. RASTtk also accommodates the batch submission of genomes and the ability to customize annotation protocols for batch submissions. This is the first major software restructuring of RAST since its inception.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

