The E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin is recruited to the 26 S proteasome via the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor Rpn13
- PMID: 25666615
- PMCID: PMC4367258
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.614925
The E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin is recruited to the 26 S proteasome via the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor Rpn13
Abstract
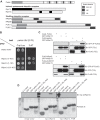
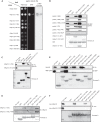
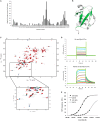
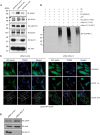
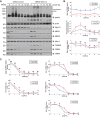
Mutations in the Park2 gene, encoding the RING-HECT hybrid E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin, are responsible for a common familial form of Parkinson disease. By mono- and polyubiquitinating target proteins, parkin regulates various cellular processes, including degradation of proteins within the 26 S proteasome, a large multimeric degradation machine. In our attempt to further elucidate the function of parkin, we have identified the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor Rpn13/ADRM1 as a parkin-interacting protein. We show that the N-terminal ubiquitin-like (Ubl) domain of parkin binds directly to the pleckstrin-like receptor for ubiquitin (Pru) domain within Rpn13. Using mutational analysis and NMR, we find that Pru binding involves the hydrophobic patch surrounding Ile-44 in the parkin Ubl, a region that is highly conserved between ubiquitin and Ubl domains. However, compared with ubiquitin, the parkin Ubl exhibits greater than 10-fold higher affinity for the Pru domain. Moreover, knockdown of Rpn13 in cells increases parkin levels and abrogates parkin recruitment to the 26 S proteasome, establishing Rpn13 as the major proteasomal receptor for parkin. In contrast, silencing Rpn13 did not impair parkin recruitment to mitochondria or parkin-mediated mitophagy upon carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone-induced mitochondrial depolarization. However, it did delay the clearance of mitochondrial proteins (TIM23, TIM44, and TOM20) and enhance parkin autoubiquitination. Taken together, these findings implicate Rpn13 in linking parkin to the 26 S proteasome and regulating the clearance of mitochondrial proteins during mitophagy.
Keywords: E3 Ubiquitin Ligase; Parkin; Parkinson Disease; Proteasome; Rpn13; Ubiquitin; Ubiquitylation (Ubiquitination).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Giasson B. I., Lee V. M. (2001) Parkin and the molecular pathways of Parkinson's disease. Neuron 31, 885–888 - PubMed
-
- Kitada T., Asakawa S., Hattori N., Matsumine H., Yamamura Y., Minoshima S., Yokochi M., Mizuno Y., Shimizu N. (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392, 605–608 - PubMed
-
- Gasser T. (2009) Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 11, e22. - PubMed
-
- Shimura H., Hattori N., Kubo S., Mizuno Y., Asakawa S., Minoshima S., Shimizu N., Iwai K., Chiba T., Tanaka K., Suzuki T. (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat. Genet. 25, 302–305 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

