Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 promotes migration and invasion of human trophoblast cells through activation of MAPK, PI3K and NOTCH signaling pathways
- PMID: 25667199
- PMCID: PMC4492406
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gav006
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 promotes migration and invasion of human trophoblast cells through activation of MAPK, PI3K and NOTCH signaling pathways
Abstract
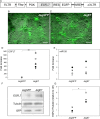
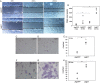
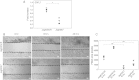
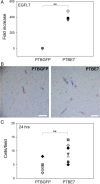
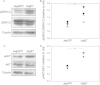
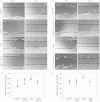
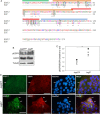
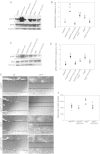
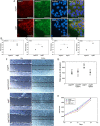
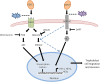
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 (Egfl7) is a gene that encodes a partially secreted protein and whose expression is largely restricted to the endothelia. We recently reported that EGFL7 is also expressed by trophoblast cells in mouse and human placentas. Here, we investigated the molecular pathways that are regulated by EGFL7 in trophoblast cells. Stable EGFL7 overexpression in a Jeg3 human choriocarcinoma cell line resulted in significantly increased cell migration and invasiveness, while cell proliferation was unaffected. Analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways showed that EGFL7 promotes Jeg3 cell motility by activating both pathways. We show that EGFL7 activates the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in Jeg3 cells, resulting in downstream activation of extracellular regulated kinases (ERKs). In addition, we provide evidence that EGFL7-triggered migration of Jeg3 cells involves activation of NOTCH signaling. EGFL7 and NOTCH1 are co-expressed in Jeg3 cells, and blocking of NOTCH activation abrogates enhanced migration of Jeg3 cells overexpressing EGFL7. We also demonstrate that signaling through EGFR and NOTCH converged to mediate EGFL7 effects. Reduction of endogenous EGFL7 expression in Jeg3 cells significantly decreased cell migration. We further confirmed that EGFL7 stimulates cell migration by using primary human first trimester trophoblast (PTB) cells overexpressing EGFL7. In conclusion, our data suggest that in trophoblast cells, EGFL7 regulates cell migration and invasion by activating multiple signaling pathways. Our results provide a possible explanation for the correlation between reduced expression of EGFL7 and inadequate trophoblast invasion observed in placentopathies.
Keywords: EGFL7; MAPK; NOTCH signaling; PI3K; trophoblast migration.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA interference-mediated knockdown of Notch-1 inhibits migration and invasion, down-regulates matrix metalloproteinases and suppresses NF-κB signaling pathway in trophoblast cells.Acta Histochem. 2014 Jun;116(5):911-9. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Acta Histochem. 2014. PMID: 24681113
-
Hyaluronan up-regulates growth and invasion of trophoblasts in an autocrine manner via PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways in early human pregnancy.Placenta. 2013 Sep;34(9):784-91. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Placenta. 2013. PMID: 23806178
-
CCN3 regulates proliferation and migration properties in Jeg3 trophoblast cells via ERK1/2, Akt and Notch signalling.Mol Hum Reprod. 2013 Apr;19(4):237-49. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gas061. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Mol Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23220688
-
EGFL7: Master regulator of cancer pathogenesis, angiogenesis and an emerging mediator of bone homeostasis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Nov;233(11):8526-8537. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26792. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29923200 Review.
-
Signal transduction in trophoblast invasion.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005;88:181-199. doi: 10.1159/000087834. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16129946 Review.
Cited by
-
Placental Dysfunction in Assisted Reproductive Pregnancies: Perinatal, Neonatal and Adult Life Outcomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 8;23(2):659. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020659. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFITM1 inhibits trophoblast invasion and is induced in placentas associated with IFN-mediated pregnancy diseases.iScience. 2023 Jun 15;26(7):107147. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107147. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37434700 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Signaling Regulating Endometrium-Blastocyst Crosstalk.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 18;21(1):23. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010023. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31861484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Different Concentrations of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor on Gene Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A in Trophoblast Tumor Cell Line.Int J Fertil Steril. 2020 Jul;14(2):116-121. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2020.6058. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Int J Fertil Steril. 2020. PMID: 32681623 Free PMC article.
-
A High-Throughput Toxicity Screen of 42 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Functional Assessment of Migration and Gene Expression in Human Placental Trophoblast Cells.Front Toxicol. 2022 Apr 25;4:881347. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.881347. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35548680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakraborty C, Barbin YP, Chakrabarti S, Chidiac P, Dixon SJ, Lala PK. Endothelin-1 promotes migration and induces elevation of [ca2+]i and phosphorylation of map kinase of a human extravillous trophoblast cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2003;201:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Cobellis L, Mastrogiacomo A, Federico E, Schettino MT, De Falco M, Manente L, Coppola G, Torella M, Colacurci N, De Luca A. Distribution of Notch protein members in normal and preeclampsia-complicated placentas. Cell Tissue Res 2007;330:527–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

