Rivastigmine from capsules to patch: therapeutic advances in the management of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia
- PMID: 25667813
- PMCID: PMC4321018
- DOI: 10.4088/PCC.14r01654
Rivastigmine from capsules to patch: therapeutic advances in the management of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia
Abstract
Objective: To discuss the pharmacology, mechanism of action, and chemical properties of the cholinesterase inhibitor (ChEI) rivastigmine; to provide a rationale for transdermal delivery and supportive clinical data, along with practical guidance on rivastigmine patch use in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia.
Data sources: Pivotal studies of rivastigmine capsules and patch were identified using PubMed and the rivastigmine US prescribing information. PubMed searches were performed in 2013 using rivastigmine as a keyword.
Study selection: English-language articles related to rivastigmine considered of relevance to primary care physicians were included.
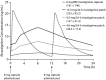
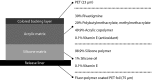
Data synthesis: Pharmacologic differences exist between rivastigmine and ChEIs. Clinical studies demonstrate symptomatic efficacy of oral rivastigmine across all stages of Alzheimer's disease and mild-to-moderate Parkinson's disease dementia. However, gastrointestinal adverse events limit access to optimal therapeutic doses. Strategies that lower maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) and prolong time to Cmax, ie, transdermal delivery, may improve tolerability. Clinical registration studies have demonstrated improved tolerability of rivastigmine 9.5-mg/24-h patch versus 6-mg twice-daily capsules in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease, and a positive benefit-risk profile of 13.3-mg/24-h versus 9.5-mg/24-h patch in patients needing enhanced efficacy. Clinical data comparing 13.3-mg/24-h versus 4.6-mg/24-h patch in severe Alzheimer's disease demonstrated efficacy on cognition and activities of daily living. These data led to approval of rivastigmine patch in severe Alzheimer's disease. Transdermal delivery also has practical advantages, including simple, once-daily administration and a visual indicator of compliance. Potential application site reactions can be minimized and need not be a barrier to treatment.
Conclusions: In addition to practical advantages, rivastigmine patch may improve clinical outcomes throughout the course of Alzheimer's disease by providing access to high-dose efficacy without compromising tolerability.
Figures
References
-
- Emre M, Poewe W, De Deyn PP, et al. Long-term safety of rivastigmine in Parkinson’s disease dementia: an open-label, randomized study. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2014;37(1):9–16. - PubMed
-
- Exelon Patch [prescribing information] East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2009. http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/exelonpatch.pdf. Updated July 2013. Accessed January 24, 2014.
-
- Exelon [prescribing information] East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2006. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2006/020823s016, 021025s008lbl.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2014.
-
- Namenda [prescribing information] St Louis, MO: Forest Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2011. http://www.frx.com/pi/namenda_pi.pdf. Updated October 2013. Accessed January 24, 2014.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
