MDM2 is an important prognostic and predictive factor for platin-pemetrexed therapy in malignant pleural mesotheliomas and deregulation of P14/ARF (encoded by CDKN2A) seems to contribute to an MDM2-driven inactivation of P53
- PMID: 25668009
- PMCID: PMC4453955
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.27
MDM2 is an important prognostic and predictive factor for platin-pemetrexed therapy in malignant pleural mesotheliomas and deregulation of P14/ARF (encoded by CDKN2A) seems to contribute to an MDM2-driven inactivation of P53
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a highly aggressive tumour that is first-line treated with a combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed. Until now, predictive and prognostic biomarkers are lacking, making it a non-tailored therapy regimen with unknown outcome. P53 is frequently inactivated in MPM, but mutations are extremely rare. MDM2 and P14/ARF are upstream regulators of P53 that may contribute to P53 inactivation.
Methods: A total of 72 MPM patients were investigated. MDM2 immunoexpression was assessed in 65 patients. MDM2 and P14/ARF mRNA expression was analysed in 48 patients of the overall collective. The expression results were correlated to overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
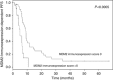
Results: OS and PFS correlated highly significantly with MDM2 mRNA and protein expression, showing a dismal prognosis for patients with elevated MDM2 expression (for OS: Score (logrank) test: P⩽0.002, and for PFS: Score (logrank) test; P<0.007). MDM2 was identified as robust prognostic and predictive biomarker for MPM on the mRNA and protein level. P14/ARF mRNA expression reached no statistical significance, but Kaplan-Meier curves distinguished patients with low P14/ARF expression and hence shorter survival from patients with higher expression and prolonged survival.
Conclusions: MDM2 is a prognostic and predictive marker for a platin-pemetrexed therapy of patients with MPMs. Downregulation of P14/ARF expression seems to contribute to MDM2-overexpression-mediated P53 inactivation in MPM patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mdm2 protein expression is strongly associated with survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Future Oncol. 2014 May;10(6):995-1005. doi: 10.2217/fon.13.261. Future Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24941985
-
Thymidylate synthase and excision repair cross-complementing group-1 as predictors of responsiveness in mesothelioma patients treated with pemetrexed/carboplatin.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;17(8):2581-90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2873. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21262916 Clinical Trial.
-
Aberrant expression of cell cycle regulatory genes predicts overall and disease free survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients.Exp Mol Pathol. 2012 Aug;93(1):154-61. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.04.001. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22504106
-
Pemetrexed therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Ann Pharmacother. 2005 Apr;39(4):678-83. doi: 10.1345/aph.1E329. Epub 2005 Mar 8. Ann Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 15755794 Review.
-
The value of pemetrexed for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a comprehensive review.Anticancer Res. 2013 Sep;33(9):3553-61. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24023280 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of Pleural Mesotheliomas for DNA-damage Repair Players by Digital Gene Expression Analysis Can Enhance Clinical Management of Patients Receiving Platin-Based Chemotherapy.J Cancer. 2016 Sep 13;7(13):1915-1925. doi: 10.7150/jca.16390. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27698933 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale copy number analysis reveals variations in genes not previously associated with malignant pleural mesothelioma.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 1;8(69):113673-113686. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22817. eCollection 2017 Dec 26. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29371938 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2 and HIF1alpha expression levels in different histologic subtypes of malignant pleural mesothelioma: correlation with pathological and clinical data.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):42053-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5974. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26544728 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib sensitivity is tissue dependent and high expression of the 20S proteasome precludes good response in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Sep 24;11:8711-8720. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S194337. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31576173 Free PMC article.
-
Double Empirical Bayes Testing.Int Stat Rev. 2020 Dec;88(Suppl 1):S91-S113. doi: 10.1111/insr.12430. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Int Stat Rev. 2020. PMID: 35356801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altomare DA, Menges CW, Xu J, Pei J, Zhang L, Tadevosyan A, Neumann-Domer E, Liu Z, Carbone M, Chudoba I, Klein-Szanto AJ, Testa JR. Losses of both products of the Cdkn2a/Arf locus contribute to asbestos-induced mesothelioma development and cooperate to accelerate tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18828. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Astoul P, Roca E, Galateau-Salle F, Scherpereel A. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: from the bench to the bedside. Respiration. 2012;83:481–493. - PubMed
-
- Bahnassy AA, Zekri AR, Abou-Bakr AA, El-Deftar MM, El-Bastawisy A, Sakr MA, El-Sherif GM, Gaafar RM. Aberrant expression of cell cycle regulatory genes predicts overall and disease free survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;93:154–161. - PubMed
-
- Barckhausen C, Roos WP, Naumann SC, Kaina B. Malignant melanoma cells acquire resistance to DNA interstrand cross-linking chemotherapeutics by p53-triggered upregulation of DDB2/XPC-mediated DNA repair. Oncogene. 2014;33:1964–1974. - PubMed
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 2009;55:611–622. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

