Lysosomal physiology
- PMID: 25668017
- PMCID: PMC4524569
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071649
Lysosomal physiology
Abstract
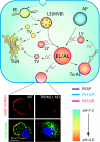
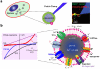
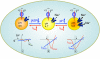
Lysosomes are acidic compartments filled with more than 60 different types of hydrolases. They mediate the degradation of extracellular particles from endocytosis and of intracellular components from autophagy. The digested products are transported out of the lysosome via specific catabolite exporters or via vesicular membrane trafficking. Lysosomes also contain more than 50 membrane proteins and are equipped with the machinery to sense nutrient availability, which determines the distribution, number, size, and activity of lysosomes to control the specificity of cargo flux and timing (the initiation and termination) of degradation. Defects in degradation, export, or trafficking result in lysosomal dysfunction and lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs). Lysosomal channels and transporters mediate ion flux across perimeter membranes to regulate lysosomal ion homeostasis, membrane potential, catabolite export, membrane trafficking, and nutrient sensing. Dysregulation of lysosomal channels underlies the pathogenesis of many LSDs and possibly that of metabolic and common neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: TFEB; TPC1; TPC2; TRPML1; lysosomal exocytosis; lysosomal storage disease; mTOR.
Figures
References
-
- Luzio JP, Pryor PR, Bright NA. Lysosomes: fusion and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:622–32. - PubMed
-
- Kolter T, Sandhoff K. Principles of lysosomal membrane digestion: stimulation of sphingolipid degradation by sphingolipid activator proteins and anionic lysosomal lipids. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005;21:81–103. - PubMed
-
- Ruivo R, Anne C, Sagne C, Gasnier B. Molecular and cellular basis of lysosomal transmembrane protein dysfunction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1793:636–49. - PubMed
-
- Saftig P, Klumperman J. Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: Trafficking meets function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:623–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

