Characteristics of fixational eye movements in amblyopia: Limitations on fixation stability and acuity?
- PMID: 25668775
- PMCID: PMC4529398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2015.01.016
Characteristics of fixational eye movements in amblyopia: Limitations on fixation stability and acuity?
Abstract
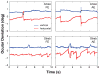
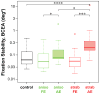
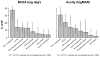
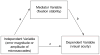
Persons with amblyopia, especially those with strabismus, are known to exhibit abnormal fixational eye movements. In this paper, we compared six characteristics of fixational eye movements among normal control eyes (n=16), the non-amblyopic fellow eyes and the amblyopic eyes of anisometropic (n=14) and strabismic amblyopes (n=14). These characteristics include the frequency, magnitude of landing errors, amplitude and speed of microsaccades, and the amplitude and speed of slow drifts. Fixational eye movements were recorded using retinal imaging while observers monocularly fixated a 1° cross. Eye position data were recovered using a cross-correlation procedure. We found that in general, the characteristics of fixational eye movements are not significantly different between the fellow eyes of amblyopes and controls, and that the strabismic amblyopic eyes are always different from the other groups. Next, we determined the primary factors that limit fixation stability and visual acuity in amblyopic eyes by examining the relative importance of the different oculomotor characteristics, adding acuity (for fixation stability) or fixation stability (for acuity), and the type of amblyopia, as predictive factors in a multiple linear regression model. We show for the first time that the error magnitude of microsaccades, acuity, amplitude and frequency of microsaccades are primary factors limiting fixation stability; while the error magnitude, fixation stability, amplitude of drifts and amplitude of microsaccades are the primary factors limiting acuity. A mediation analysis showed that the effects of error magnitude and amplitude of microsaccades on acuity could be explained, at least in part, by their effects on fixation stability.
Keywords: Amblyopia; Fixation stability; Fixational eye movements; Microsaccades; Slow drifts; Visual acuity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bedell HE, Flom MC, Barbeito R. Spatial aberrations and acuity in strabismus and amblyopia. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 1985;26:909–916. - PubMed
-
- Bedell HE, Yap YL, Flom MC. Fixational drift and nasal-temporal pursuit asymmetries in strabismic amblyopes. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 1990;31:968–976. - PubMed
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Bonneh YS, Sagi D, Polat U. Spatial and temporal crowding in amblyopia. Vision Research. 2007;47:1950–1962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

