Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer
- PMID: 25669979
- PMCID: PMC4467160
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3216
Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer
Abstract
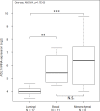
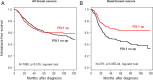
Expression of programmed cell death receptor ligand 1 (PDL1) has been scarcely studied in breast cancer. Recently PD1/PDL1-inhibitors have shown promising results in different carcinomas with correlation between PDL1 tumor expression and responses. We retrospectively analyzed PDL1 mRNA expression in 45 breast cancer cell lines and 5,454 breast cancers profiled using DNA microarrays. Compared to normal breast samples, PDL1 expression was upregulated in 20% of clinical samples and 38% of basal tumors. High expression was associated with poor-prognosis features (large tumor size, high grade, ER-negative, PR-negative, ERBB2-positive status, high proliferation, basal and ERBB2-enriched subtypes). PDL1 upregulation was associated with biological signs of strong cytotoxic local immune response. PDL1 upregulation was not associated with survival in the whole population, but was associated with better metastasis-free and overall specific survivals in basal tumors, independently of clinicopathological features. Pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy was higher in case of PDL1 upregulation (50% versus 21%). In conclusion, PDL1 upregulation, more frequent in basal breast cancers, was associated with increased T-cell cytotoxic immune response. In this aggressive subtype, upregulation was associated with better survival and response to chemotherapy. Reactivation of dormant tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes by PDL1-inhibitors could represent promising strategy in PDL1-upregulated basal breast cancer.
Keywords: PDL1; breast cancer; chemotherapy; immune response; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M, Muller BM, Komor M, Budczies J, Darb-Esfahani S, Kronenwett R, Hanusch C, von Torne C, Weichert W, Engels K, et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(1):105–113. - PubMed
-
- Ali HR, Provenzano E, Dawson SJ, Blows FM, Liu B, Shah M, Earl HM, Poole CJ, Hiller L, Dunn JA, Bowden SJ, Twelves C, Bartlett JM, et al. Association between CD8+ T-cell infiltration and breast cancer survival in 12,439 patients. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(8):1536–1543. - PubMed
-
- Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Bono P, Kataja V, Desmedt C, Piccart MJ, Loibl S, Denkert C, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(8):1544–1550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

