Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 signals through antioxidant glutathione peroxidase 1 to regulate redox homeostasis and tumor growth
- PMID: 25670081
- PMCID: PMC4325424
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.12.006
Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 signals through antioxidant glutathione peroxidase 1 to regulate redox homeostasis and tumor growth
Abstract
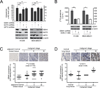
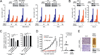
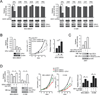
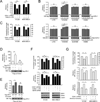
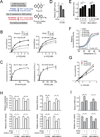
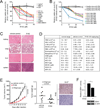
How mitochondrial glutaminolysis contributes to redox homeostasis in cancer cells remains unclear. Here we report that the mitochondrial enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GDH1) is commonly upregulated in human cancers. GDH1 is important for redox homeostasis in cancer cells by controlling the intracellular levels of its product alpha-ketoglutarate and subsequent metabolite fumarate. Mechanistically, fumarate binds to and activates a reactive oxygen species scavenging enzyme glutathione peroxidase 1. Targeting GDH1 by shRNA or a small molecule inhibitor R162 resulted in imbalanced redox homeostasis, leading to attenuated cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Boonstra J, Post JA. Molecular events associated with reactive oxygen species and cell cycle progression in mammalian cells. Gene. 2004;337:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

