Enteroendocrine cells are generated from stem cells through a distinct progenitor in the adult Drosophila posterior midgut
- PMID: 25670791
- PMCID: PMC4325374
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.113357
Enteroendocrine cells are generated from stem cells through a distinct progenitor in the adult Drosophila posterior midgut
Abstract
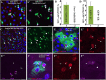
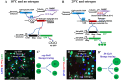
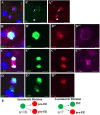
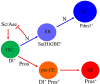
Functional mature cells are continually replenished by stem cells to maintain tissue homoeostasis. In the adult Drosophila posterior midgut, both terminally differentiated enterocyte (EC) and enteroendocrine (EE) cells are generated from an intestinal stem cell (ISC). However, it is not clear how the two differentiated cells are generated from the ISC. In this study, we found that only ECs are generated through the Su(H)GBE(+) immature progenitor enteroblasts (EBs), whereas EEs are generated from ISCs through a distinct progenitor pre-EE by a novel lineage-tracing system. EEs can be generated from ISCs in three ways: an ISC becoming an EE, an ISC becoming a new ISC and an EE through asymmetric division, or an ISC becoming two EEs through symmetric division. We further identified that the transcriptional factor Prospero (Pros) regulates ISC commitment to EEs. Our data provide direct evidence that different differentiated cells are generated by different modes of stem cell lineage specification within the same tissues.
Keywords: Drosophila; Intestinal stem cell; Pre-enteroendocrine cell; Prospero; Secretory enteroendocrine cell.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

