Ularitide for the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure: from preclinical to clinical studies
- PMID: 25670819
- PMCID: PMC4368857
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu484
Ularitide for the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure: from preclinical to clinical studies
Abstract
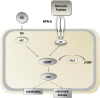
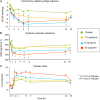
The short- and long-term morbidity and mortality in acute heart failure is still unacceptably high. There is an unmet need for new therapy options with new drugs with a new mode of action. One of the drugs currently in clinical testing in Phase III is ularitide, which is the chemically synthesized form of the human natriuretic peptide urodilatin. Urodilatin is produced in humans by differential processing of pro-atrial natriuretic peptide in distal renal tubule cells. Physiologically, urodilatin appears to be the natriuretic peptide involved in sodium homeostasis. Ularitide exerts its pharmacological actions such as vasodilation, diuresis, and natriuresis through the natriuretic peptide receptor/particulate guanylate cyclase/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway. In animal models of heart failure as well as Phase I and II clinical studies in heart failure patients, ularitide demonstrated beneficial effects such as symptom relief and vasodilation, while still preserving renal function. Subsequently, the pivotal acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) Phase III study, called TRUE-AHF, was started with the objectives to evaluate the effects of ularitide infusion on the clinical status and cardiovascular mortality of patients with ADHF compared with placebo. This review summarizes preclinical and clinical data supporting the potential use of ularitide in the treatment of ADHF.
Keywords: Acute decompensated heart failure; Diuresis; Guanylate cyclase; Natriuresis; Ularitide; Vasodilation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



References
-
- Forssmann WG, Richter R, Meyer M. The endocrine heart and natriuretic peptides: histochemistry, cell biology, and functional aspects of the renal urodilatin system. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998;110:335–357. - PubMed
-
- Saba SR, Ramirez G, Vesely DL. Immunocytochemical localization of ProANF 1-30, ProANF 31-67, atrial natriuretic factor and urodilatin in the human kidney. Am J Nephrol. 1993;13:85–93. - PubMed
-
- Schulz-Knappe P, Forssmann K, Herbst F, Hock D, Pipkorn R, Forssmann WG. Isolation and structural analysis of “urodilatin”, a new peptide of the cardiodilatin-(ANP)-family, extracted from human urine. Klin Wochenschr. 1988;66:752–759. - PubMed
-
- Goetz KL. Renal natriuretic peptide (urodilatin?) and atriopeptin: evolving concepts. Am J Physiol. 1991;261(6 Pt 2):F921–F932. - PubMed
-
- Nagase M, Katafuchi T, Hirose S, Fujita T. Tissue distribution and localization of natriuretic peptide receptor subtypes in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1997;15:1235–1243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

