Differential expression and prognostic value of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms
- PMID: 25671300
- PMCID: PMC4413658
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3242
Differential expression and prognostic value of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms
Abstract
Introduction: For many tumors, the overexpression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 is associated with increased malignancy and poor patient outcomes. However, comprehensive data for neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung are still lacking.
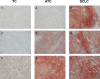
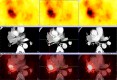
Methods: CXCR4 expression was evaluated in a panel of bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms (BP-NEN) comprising typical carcinoids (n = 26), atypical carcinoids (n = 30), and small cell lung cancers (SCLC, n = 34). Samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using the novel monoclonal rabbit anti-human CXCR4 antibody UMB-2 and by qRT-PCR. The expression was correlated with clinical data and overall patient survival.
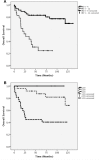
Results: CXCR4 was predominantly localized at the plasma membrane of the tumor cells. CXCR4 was expressed with a high intensity in almost all of the 30 SCLC samples. In contrast, it was detected infrequently and with low intensity in the typical carcinoid and atypical carcinoid samples. There was a significant correlation between the immunohistochemistry and qRT-PCR data. Additionally, there was a significant negative relationship between CXCR4 expression and overall survival.
Conclusions: With increasing malignancy, BP-NEN clearly differ in the extent of CXCR4 expression. As in other tumor entities, CXCR4 overexpression significantly correlates with negative patient outcome. Due to its particular high expression rate in SCLC, CXCR4 may serve as a promising new target for diagnostic and pharmacological intervention as well as for peptide receptor-based radionuclide therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Kaemmerer D. received support for travelling to meetings by the companies Pfizer and Ipsen. All other authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Fazio N, Abdel-Rahman O, Spada F, Galdy S, De Dosso S, Capdevila J, Scarpa A. RAF signaling in neuroendocrine neoplasms: From bench to bedside. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A, Malfertheiner MV, Modlin IM. Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer. 2008;113(1):5–21. - PubMed
-
- Horsch D, Sayeg Y, Bonnet R, Kaemmerer D, Presselt N, Baum RP. [Expert dialogue: neuroendocrine tumours of the lungs and gastroenteropancreatic system] Pneumologie. 2012;66(1):44–48. - PubMed
-
- Naalsund A, Rostad H, Strom EH, Lund MB, Strand TE. Carcinoid lung tumors - incidence, treatment and outcomes: a population-based study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;39(4):565–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

