Therapeutic targeting of aldosterone: a novel approach to the treatment of glomerular disease
- PMID: 25671776
- PMCID: PMC4356246
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20140432
Therapeutic targeting of aldosterone: a novel approach to the treatment of glomerular disease
Abstract
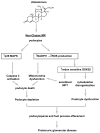
Numerous studies have established a role for mineralocorticoids in the development of renal fibrosis. Originally, the research focus for mineralocorticoid-induced fibrosis was on the collecting duct, where 'classical' mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) involved with electrolyte transport are present. Epithelial cells in this segment can, under selected circumstances, also respond to MR activation by initiating pro-fibrotic pathways. More recently, 'non-classical' MRs have been described in kidney cells not associated with electrolyte transport, including mesangial cells and podocytes within the glomerulus. Activation of MRs in these cells appears to lead to glomerular sclerosis. Mechanistically, aldosterone induces excess production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress in glomerular cells through activation of NADPH oxidase. In mesangial cells, aldosterone also has pro-apoptotic, mitogenic and pro-fibrogenic effects, all of which potentially promote active remodelling and expansion of the mesangium. Although mitochondrial dysfunction seems to mediate the aldosterone-induced mesangial apoptosis, the ROS dependent epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation is probably responsible for aldosterone-induced mesangial mitosis and proliferation. In podocytes, mitochondrial dysfunction elicited by oxidative stress is an early event associated with aldosterone-induced podocyte injury. Both the p38 MAPK (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase) signalling and the redox-sensitive glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)3β pathways are centrally implicated in aldosterone-induced podocyte death. Aldosterone-induced GSK3β over-activity could potentially cause hyperphosphorylation and over-activation of putative GSK3β substrates, including structural components of the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) pore, all of which lead to cell injury and death. Clinically, proteinuria significantly decreases when aldosterone inhibitors are included in the treatment of many glomerular diseases further supporting the view that mineralocorticoids are important players in glomerular pathology.
Figures


References
-
- Selye H. Anticortisol action of aldosterone. Science. 1955;121:368–369. - PubMed
-
- Funder JW, Feldman D, Edelman IS. The roles of plasma binding and receptor specificity in the mineralocorticoid action of aldosterone. Endocrinology. 1973;92:994–1004. - PubMed
-
- Farman N, Kusch M, Edelman IS. Aldosterone receptor occupancy and sodium transport in the urinary bladder of Bufo marinus. Am J Physiol. 1978;235:C90–96. - PubMed
-
- Rossier BC, Wilce PA, Edelman IS. Spironolactone antagonism of aldosterone action on Na+ transport and RNA metabolism in toad bladder epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1977;32:177–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

