Spitz nevi in the classic histopathological pattern--lamb in wolf`s clothing
- PMID: 25672303
- PMCID: PMC4323702
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153310
Spitz nevi in the classic histopathological pattern--lamb in wolf`s clothing
Abstract
Spitz nevus is a benign melanocytic lesion and also one of the main differential diagnosis of melanoma. A descriptive and retrospective study of surgical specimens from patients with a diagnosis of Spitz nevus was conducted at two institutions in Niterói - RJ. 32 cases were analyzed. The most frequent histological subtype was compound (60 %), with a predominance of epithelioid cells (17 cases - 53%). Pagetoid spread was observed in 21 cases (68%). Maturation of melanocytes was present in 13 cases (81%). Kamino bodies were found in eight cases (25%). Atypical melanocytes were present in 18 cases (56%). Mitoses were present in 11 cases (34%). Detailed knowledge of the classical form of Spitz nevi is essential for the differential diagnosis with melanoma. However, no single criterium is definitive in the differential diagnosis between Spitz nevus and melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
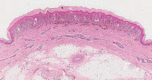
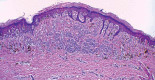

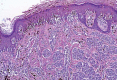
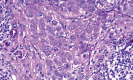
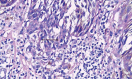
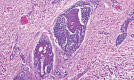
Similar articles
-
Clinical and histopathological features of pagetoid Spitz nevi of the thigh.J Cutan Pathol. 2020 Dec;47(12):1143-1149. doi: 10.1111/cup.13854. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Cutan Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32829516
-
Spitz nevus in a Hispanic population: a clinicopathological study of 130 cases.Am J Dermatopathol. 2010 May;32(3):267-275. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181c52b99. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010. PMID: 20098300
-
[Desmoplastic Spitz nevus: a histopathological review and comparison with desmoplastic melanoma].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009 Oct;136(10):689-95. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009. PMID: 19801251 French.
-
[Spitz nevus and Reed nevus: simulating melanoma in adults].Pathologe. 1998 Nov;19(6):403-11. doi: 10.1007/s002920050304. Pathologe. 1998. PMID: 9885003 Review. German.
-
Classic and atypical Spitz nevi: review of the literature.Cutis. 2007 Feb;79(2):141-6. Cutis. 2007. PMID: 17388217 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Landscape of Spitzoid Neoplasms Impacting Patient Management.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 13;5:344. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00344. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30619857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative histopathological and immunophenotypical characterisation of the inflammatory microenvironment in spitzoid melanocytic neoplasms.Histopathology. 2021 Mar;78(4):607-626. doi: 10.1111/his.14259. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Histopathology. 2021. PMID: 32970867 Free PMC article.
-
The Spectrum of Spitz Melanocytic Lesions: From Morphologic Diagnosis to Molecular Classification.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:889223. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889223. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35747831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinico-dermoscopic and Histopathological Evaluation of Benign Skin, Soft Tissue and Appendageal Tumours of Skin: A Cross-sectional Study from a Tertiary Care Hospital.Indian J Dermatol. 2025 Jan-Feb;70(1):50. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_461_24. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Indian J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39896304 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography confirms non-malignant pigmented lesions in phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica using a support vector machine learning algorithm.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Jun;29(6):e13377. doi: 10.1111/srt.13377. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37357662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mooi J, Krausz T. Spitz nevus versus spitzoid melanoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Yoradjian A, Enokihara MM, Paschoal FM. Spitz nevus and Reed nevus. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman AB, Mendonca AMN. Ackerman AB, Guo Y, Lazova R, Kaddu S. Differential Diagnosis in Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. New York: Ardor Scribendi; 2001. Spitz's Nevus, Compound Type vs. Malignant Melanoma; pp. 1:146–1:149.
-
- Mooi J. Spitz nevus and its histologic simulators. Adv Anat Pathol. 2002;9:209–221. - PubMed
-
- Requena C, Requena L, Kutzner H, Sanchez Yus E. Spitz nevus: a clinicopathological study of 349 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:107–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
